Who are Data Scientists?
Learn who data scientists are, what they do, key skills, career paths, salaries in 2026, and real-world applications of data science.

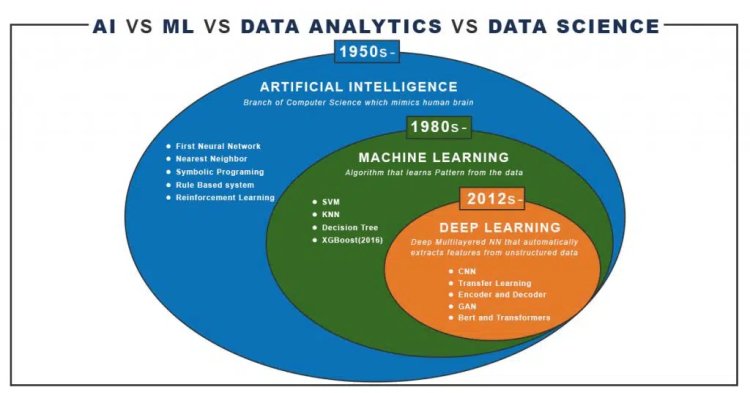
In the digital economy, data has become the most valuable business asset. Companies such as Netflix, Google, Amazon, and Facebook rely heavily on data-driven systems to personalize content, predict user behavior, prevent fraud, and automate decision-making. These intelligent systems are built using Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Natural Language Processing (NLP). However, many aspiring professionals struggle to understand how these technologies differ and how they connect to Data Science.
A Data Scientist plays a central role in this ecosystem. The end goal of a data scientist is not just to analyze data but to build intelligent products that learn from user behavior and improve automatically. With increasing adoption of AI across industries, data science has become one of the most strategic and high-growth career paths globally.
A report by McKinsey Global Institute states that data-driven organizations are 23 times more likely to acquire customers and 6 times more likely to retain them through predictive analytics.
This article explains AI, ML, DL, NLP, and Data Science, their interconnections, what data scientists do, career paths, and salaries in 2026. Let’s start with definitions first.
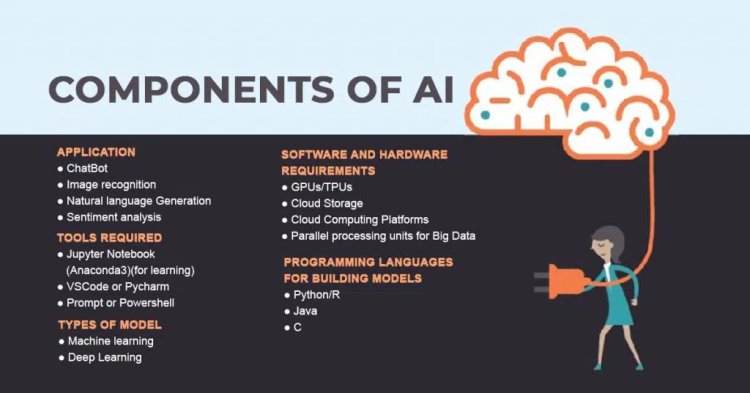
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
The domain of computer science enables the machine to think without human intervention, a machine can be software, an application, like Instagram, self-driving car and many more. AI is only math and scientific exercise, but when it became computational, it began to solve human problems formalized into a subset of computing. Artificial intelligence has changed the original computational statistics paradigm to the modern idea that machines could mimic actual human capabilities, such as deciding and performing more “human” tasks. Modern AI into two categories
- General AI – Planning, decision making, identifying objects, recognizing sounds, social &
business transactions - Applied AI – driverless/ Autonomous car or machine smartly trade stocks.

Refer to these articles:
- Secure Data Science Pipelines: Preventing Data Leakage and Attacks
- Data Science vs Cyber Security: Which Has Better Future?
- Role of Data Science in Smart Cities and Internet of Things (IoT)
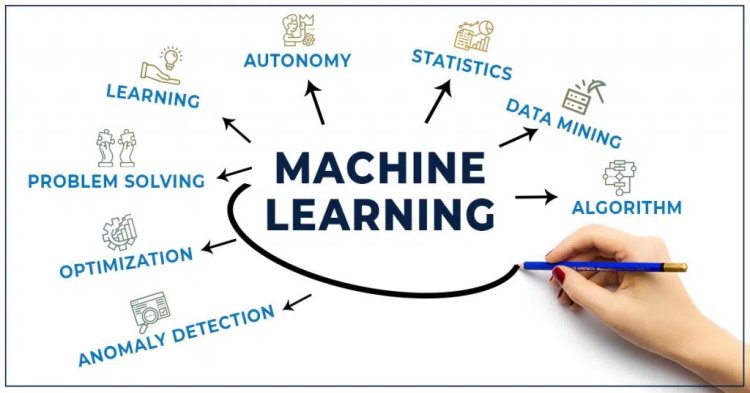
What Is Machine Learning (ML)?
The AI tool which uses statistics, visualization, predictive analytics, forecasting to predict the future. Instead of engineers “teaching” or programming computers to possess what they have
to carry out tasks, that perhaps computers could teach themselves – learn something without being explicitly programmed to try to do so. ML is a subset of AI where based on more data, it can change actions and response, which will make them more well organized, adaptable and scalable. e.g., navigation apps and recommendation engines.
The further classification of ML includes
- Supervised
- Unsupervised
- Reinforcement learning
What Is Deep Learning (DL)?
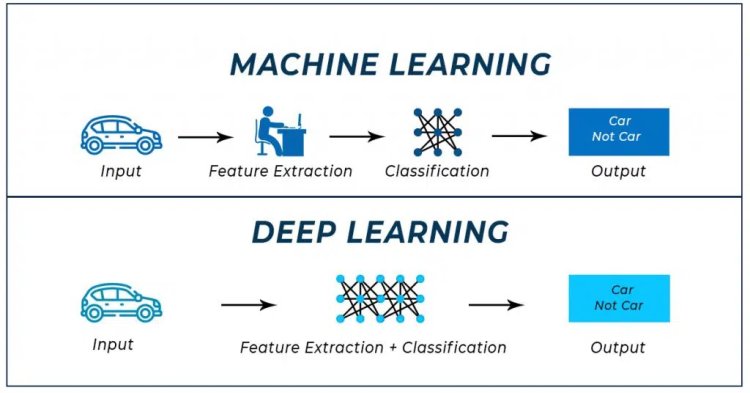
It is a subset of machine learning which mimics the human brain and makes machines learn. It is a technique for implementing ML.
ML provides the specified output from a given input, but DL reads the input and applies it to different data. In ML, we will easily classify the flower based upon the features. Suppose you want a machine to look at an image and determine what it represents to the human eye, whether a face, flower, landscape, truck, building, etc.
Machine learning isn’t sufficient for this task because machine learning can only produce an output from a knowledge set – whether consistent with a known algorithm or supported the inherent structure of the data. You might be ready to use machine learning to work out whether a picture was of an “X” – a flower, say – and it might learn and obtain more accuracy. But that output is binary (yes/no) and depends on the algorithm, not the info. In the image recognition case, the result isn’t binary and not hooked into the algorithm. The neural network performs nanoscopic calculations with computation on many layers. Neural networks also support weighting data for ‘confidence. These results in a probabilistic system, vs. deterministic, and may handle tasks that we expect of as requiring more ‘human-like judgment.
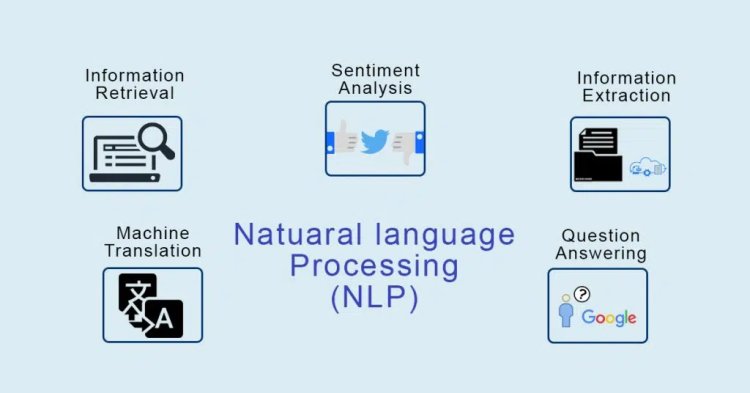
What Is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
It is part of both machine learning as well as deep learning and mainly focuses on text, voice data. Think about how much text you see each day:
- Signs
- Menus
- SMS
- Web Pages
- and so much more…
Now, let’s talk about Data Science – the technology that powers AI applications and helps businesses make smarter decisions. By using Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Natural Language Processing (NLP), data science transforms raw data into insights and intelligent systems that learn and improve over time.
What Is Data Science?
The technology which uses ML or DL or NLP to create AI applications is known as Data Science.The task done by a Data Scientist is
- Creating AI applications
- Collaborating with the DevOps team to make the application live.
- Model Retraining
- Data Analysis
Data science has many tools, techniques, and algorithms called from these fields, plus others –to handle Big Data. The aim of knowledge science, somewhat like machine learning, i.e to make accurate predictions and to automate and perform transactions in real-time, such as purchasing internet traffic or automatically generating content. Data science depends less on math and coding and more on data and building new systems to process the data. Emphasis on the fields of data integration, distributed architecture, automated machine learning, data visualization, data engineering, and automated data-driven decisions, data science can cover an entire spectrum of data processing, not only the algorithms or statistics associated with data.
Who Are Data Scientists?
A data scientist is a professional who combines skills from mathematics, statistics, programming, and business knowledge to analyze complex datasets. Their main responsibility is to extract meaningful information from structured and unstructured data and use it to solve real-world problems.
Unlike traditional data analysts who mainly focus on reporting and dashboards, data scientists use advanced statistical techniques and machine learning algorithms. They build predictive models, automate decisions, and design systems that learn from data.
Data scientists work in almost every industry, including healthcare, finance, retail, telecommunications, manufacturing, and government. Any organization that relies on data-driven decision-making requires data scientists to stay competitive.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment of data scientists is projected to grow 35% from 2022 to 2032, much faster than the average for all occupations
Refer to these articles:
- Why Bias, Fairness, and Transparency Are the New Metrics in Data Science
- How LLMs Are Transforming Data Science Careers in 2026
- Data Mesh vs Data Fabric in 2026: Choosing the Right Data Architecture
Data Scientist Responsibilities and Daily Workflow
The work of a data scientist follows a structured process, starting from understanding a problem to delivering insights that support business actions.
1. Data Collection
Data scientists gather data from various sources such as databases, cloud storage, APIs, IoT devices, and web platforms. The data may be structured (tables, spreadsheets) or unstructured (text, images, videos).
2. Data Cleaning and Preparation
Raw data often contains missing values, duplicate records, and incorrect entries. Data scientists clean and preprocess the data by handling missing values, removing noise, and transforming variables into usable formats.
3. Data Exploration and Analysis
Using statistical methods and visualization tools, data scientists explore the data to understand patterns, trends, and relationships. This step helps them identify key factors that influence outcomes.
4. Model Building and Machine Learning
Data scientists apply machine learning algorithms such as regression, classification, clustering, and neural networks to build predictive or descriptive models. These models can forecast sales, detect fraud, or recommend products.
5. Data Visualization and Communication
Insights must be clearly communicated to decision-makers. Data scientists use charts, dashboards, and reports to explain findings in a simple and understandable way.
6. Business Problem-Solving
The ultimate goal of a data scientist is to use data to solve business problems. This may include improving customer experience, reducing operational costs, or increasing revenue.
Key Skills Required to Become a Data Scientist
To succeed as a data scientist, professionals need a balanced combination of technical expertise and soft skills that enable them to analyze data, build predictive models, and translate insights into business value.
Technical Skills
- Programming: Python and R are the most popular programming languages in data science. Python is widely used due to its libraries such as NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, and Scikit-learn.
- Statistics and Mathematics: Knowledge of probability, hypothesis testing, linear algebra, and calculus is essential for building and evaluating models.
- Machine Learning: Data scientists must understand supervised and unsupervised learning techniques, including linear regression, decision trees, random forests, support vector machines, and neural networks.
- Databases and SQL: SQL is used to extract data from relational databases. Familiarity with NoSQL databases is also useful for handling large and unstructured data.
- Big Data Tools: Tools like Hadoop and Spark help process large datasets efficiently.
Non-Technical Skills
- Communication: Data scientists must explain technical results in simple language for non-technical stakeholders.
- Critical Thinking: They must interpret results correctly and avoid incorrect conclusions.
- Business Understanding: Domain knowledge helps data scientists link insights to real-world goals.
Refer to these articles:
- Data Analyst vs Data Scientist vs Data Engineer
- Data Engineer vs Analytics Engineer vs Data Analyst
- Data Scientist vs ML Engineer vs AI Engineer
Average salary of a data scientist globally
The average salary of a data scientist demonstrates the growing demand and value of this role worldwide. Here’s a detailed country-wise breakdown:
- India: The average salary of a data scientist in India varies by experience, with entry‑level professionals typically earning around ₹8 LPA – ₹12 LPA, mid‑level data scientists earning about ₹18 LPA – ₹30 LPA, and senior data scientists commanding ₹35 LPA – ₹55 LPA or more as they lead data and AI initiatives in top tech hubs like Bengaluru and Mumbai. Glassdoor data shows that the average annual salary for a data scientist in India can exceed ₹15 LPA, with top professionals earning significantly higher based on skills and roles.
- United States: The average salary of a data scientist in the U.S. is approximately $130,140 per year, according to salary trend reports and industry pay research. Senior data scientists in leading tech markets often earn well above this range as demand for advanced analytics and AI expertise grows. (Source: Indeed)
- Germany: The average salary of a data scientist in Germany typically falls between roughly €60,000 – €80,000 per year, reflecting variations by experience and city, with higher pay in major tech and industrial centers such as Berlin and Munich. (Source: Glassdoor)
- United Kingdom: The average salary of a data scientist in the UK is about £61,000 per year, with variation by location and company; data professionals in London and larger enterprises often see salaries toward the upper end of the range. (Source: Glassdoor)
- Canada: The average salary of a data scientist in Canada is approximately CA$102,000 per year, according to recent pay data shared by professionals, with actual pay depending on experience, city, and industry sector. (Source: Glassdoor)
These figures underscore that data science remains one of the most lucrative and globally in‑demand technology careers in 2026, with salaries linked closely to experience, region, and industry demand.
According to IBM, the demand for data scientists is projected to grow by 28% globally by 2030, reflecting the increasing importance of professionals who can transform raw data into actionable insights.

Career Path & Roles in Data Science
Data science offers multiple parallel career trajectories:
- Data Analyst: Entry-level role focusing on data collection, reporting, visualization, and dashboard creation. They help businesses understand trends, patterns, and insights from structured data, providing actionable recommendations.
- Data Scientist: Builds predictive models, AI-powered solutions, and intelligent applications. Uses machine learning, deep learning, and statistical techniques to solve complex business problems and support data-driven decision-making.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Specializes in implementing ML and deep learning models at scale, optimizing algorithms, and deploying AI solutions in production environments. Ensures models perform efficiently and reliably.
- AI Specialist: Develops advanced AI products, including natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and recommendation systems. Works on cutting-edge applications for enterprises and consumer products.
- Data Architect: Designs, builds, and maintains robust data infrastructure and pipelines. Ensures seamless data flow, storage, and integration across large-scale enterprise systems.
- Chief Data Officer (CDO): Leads enterprise-wide data strategy, governance, and analytics initiatives, aligning data projects with organizational goals and driving ROI through data-driven decision-making.

Real-World Applications of Data Science in 2026
Data science is no longer a niche field—it powers intelligent systems that touch every aspect of modern life. By combining Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Natural Language Processing (NLP), data scientists create solutions that improve business efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation. Here are some of the most impactful real-world applications:
- Recommendation Engines: Netflix, Amazon, and Spotify use ML to provide personalized content and product recommendations, boosting engagement and sales.
- Fraud Detection: Banks and fintech platforms analyze transactions with AI to detect anomalies and prevent financial fraud.
- Healthcare Analytics: ML and NLP help predict diseases, optimize treatments, and analyze medical data for better patient outcomes.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Tesla and Waymo use deep learning and sensor analytics to enable self-driving cars.
- Chatbots & Voice Assistants: ChatGPT, Siri, and Alexa rely on NLP and ML to understand and respond to human language, improving customer service.
- Retail Analytics: Companies like Walmart use predictive analytics to forecast demand and personalize shopping experiences.
- Predictive Maintenance: Manufacturing firms use IoT data and ML to predict equipment failures and reduce downtime.
Data scientists are the architects of intelligent systems. By combining Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Natural Language Processing with data engineering and business insight, they transform raw data into smart applications that shape modern life.
With strong market demand, high salary potential, and relevance across industries, data science continues to be one of the most future-proof careers in technology. Understanding how these technologies work together is the first step toward building a successful data science career.
For those looking to start or advance their career, DataMites Institute offers a comprehensive Data Science Course in Hyderabad. The program covers AI, ML, DL, NLP, and practical projects, equipping students with industry-ready skills to become proficient data scientists and excel in the rapidly growing data-driven job market.
