Key Skills Every Data Analyst Needs: From SQL to Data Visualization

As businesses increasingly rely on data to guide their decisions, the role of the data analyst has gained unprecedented significance. In fact, according to a report by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the employment of data analysts is projected to grow by 31% from 2020 to 2030, much faster than the average for other occupations.
In this blog post, we will delve into the vital skills that every aspiring data analyst should possess. Understanding the technical and analytical capabilities required will empower you to navigate the complex world of data analysis effectively. Additionally, we will explore the impact of these skills across various industries and how they contribute to informed decision-making. By the end, you will have a comprehensive guide to the essential skills needed to thrive as a data analyst.
Understanding the Role of a Data Analyst
A data analyst is a specialist who gathers, organizes, and interprets data to assist organizations in making data-driven decisions. The role combines technical expertise with analytical thinking, making it a cornerstone of modern business intelligence. Data analysts work with large datasets to extract meaningful insights, identify trends, and provide actionable recommendations.
Responsibilities and Tasks
The daily tasks of a data analyst can differ greatly depending on the organization and the industry in which they work. However, some common tasks include:
- Data Collection: Gathering data from various sources, including databases, surveys, and web analytics.
- Data Cleaning: Ensuring the data is accurate, complete, and formatted correctly for analysis.
- Data Analysis: Using statistical techniques and tools to analyze data and draw conclusions.
- Reporting: Developing visual representations and reports to communicate insights to stakeholders.
Organizations across various sectors, including finance, healthcare, marketing, and technology, rely on data analysts to leverage data for strategic advantages. In every industry, the ability to interpret data accurately can drive innovation and improve outcomes.
Refer these articles:
The Importance of Data Analysts in Organizations
Data analysts play a crucial role in organizations by transforming raw data into actionable insights that drive strategic decision-making. Here are several essential reasons that underscore their significance:
Driving Business Decisions
Data analysts are essential in influencing and guiding business strategies. By translating complex data into clear insights, they enable organizations to make evidence-based decisions. For example, a retail chain might analyze sales data to determine which products are underperforming, allowing them to adjust inventory and marketing strategies accordingly.
Identifying Trends and Patterns
Through rigorous analysis, data analysts identify trends and patterns that can influence business strategies. For instance, a healthcare organization might track patient data over time to identify emerging health issues, allowing for timely interventions. This ability to spot trends can be a game-changer for businesses looking to stay competitive.
Improving Operational Efficiency
Data analysis is also instrumental in enhancing operational efficiency. By analyzing both processes and results, analysts can identify areas of delay and inefficiency. This leads to informed decisions that optimize resource allocation and reduce costs, ultimately improving profitability.
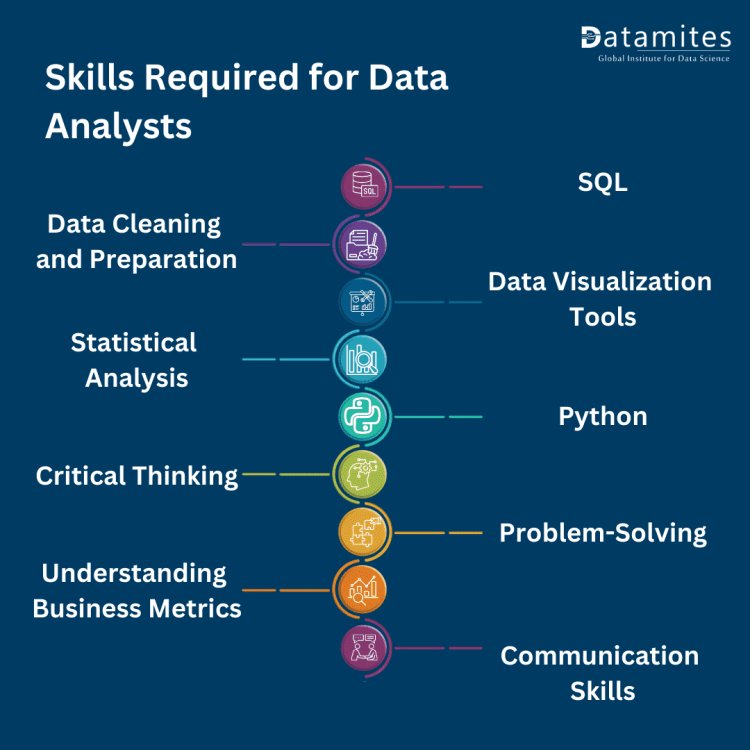
Core Skills Required for Data Analysts
To excel as a data analyst, one must develop a diverse skill set encompassing both technical and analytical capabilities. Below are the key skills essential for success in this field.
A. Technical Skills
SQL (Structured Query Language)
SQL is an essential skill for anyone pursuing a career as a data analyst. It allows analysts to interact with databases to extract and manipulate data. Mastering SQL is crucial for performing complex queries and managing large datasets.
Key SQL Concepts:
- SELECT: Tasked with retrieving data from a database.
- JOIN: Merges rows from multiple tables by using a common column as a link.
- GROUP BY: Aggregates data into summary rows, often used with functions like COUNT or SUM.
Data Cleaning and Preparation
Before any analysis can occur, data must be cleaned and prepared. This process includes removing duplicates, handling missing values, and ensuring data consistency. A well-prepared dataset is essential for producing accurate and reliable results.
Techniques for Data Cleaning:
- Handling Missing Data: Using imputation or removing incomplete records.
- Data Transformation: Transforming data into an appropriate format for analysis.
Statistical Analysis
A solid grasp of statistical principles is essential for making sense of data. Analysts must be familiar with key metrics such as mean, median, standard deviation, and correlation. Statistical analysis enables us to derive insights and forecast outcomes from data.
Common Statistical Tools:
- Regression Analysis: Used for forecasting and understanding relationships between variables.
- Hypothesis Testing: Helps in making decisions based on sample data.
Programming Skills
Programming languages like Python and R have become indispensable in data analysis. They offer powerful libraries and frameworks that streamline the data analysis process.
Popular Libraries:
- Python: Utilizing Pandas for data manipulation, Matplotlib for visualizations, and SciPy for advanced scientific computations.
- R: Utilize dplyr for transforming and manipulating data, while leveraging ggplot2 for creating visual representations of that data.
Data Visualization
Data visualization is crucial for communicating findings effectively. Well-designed visualizations can make complex data comprehensible and highlight key insights.
Popular Tools:
- Tableau: Provides robust visualization features alongside an intuitive interface.
- Power BI: Integrates well with Microsoft products and provides robust reporting features.
- Matplotlib: A Python library designed for generating static, interactive, and animated visual representations.
B. Analytical Skills
Critical Thinking
Data analysts must possess strong critical thinking skills. This involves questioning data sources, evaluating the reliability of findings, and being able to distinguish between correlation and causation.
Examples of Critical Thinking:
- Analyzing whether a significant change in sales is due to a marketing campaign or seasonal variations.
- Assessing the credibility of a dataset before drawing conclusions.
Problem-Solving
Data analysts often face complex business problems that require innovative solutions. They need to approach these challenges methodically, utilizing their analytical skills to identify root causes and propose actionable solutions.
Approach to Problem-Solving:
- Define the Problem: Articulate the problem clearly and express it in a distinct manner.
- Analyze Data: Collect pertinent information to aid in the decision-making process.
- Implement Solutions: Develop and test solutions, then evaluate their effectiveness.
C. Business Acumen
Understanding Business Metrics
A skilled data analyst must understand the critical key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to their particular industry. This understanding enables them to connect data analysis with business goals, ensuring that their insights lead to actionable outcomes.
Common KPIs:
- Sales Growth: Measures the ability to increase revenue over time.
- Customer Retention Rate: Indicates how well a company retains its customers.
Communication Skills
Effective communication is paramount in data analysis. Analysts must convey their findings clearly to both technical and non-technical stakeholders. This includes creating reports and presentations that highlight key insights and recommendations.
Tips for Effective Communication:
- Know Your Audience: Tailor your message to the technical proficiency of your audience.
- Use Visuals: Incorporate graphs and charts to make data more accessible.
Refer these articles:
- What is Datamites Certified Data Analyst Certification
- Data Analyst Career Scope in India
- How to Become A Data Analyst
Career Opportunities of Data Analyst
The career path for data analysts offers multiple opportunities for growth, and professionals can work in a wide range of industries, depending on their skills and interests. Here’s a breakdown of key aspects:
Typical Career Progression
Entry-Level Data Analyst: The journey often begins here, where analysts work on cleaning and interpreting data, generating reports, and performing basic analyses. Proficiency in Excel, SQL, and data visualization tools like Tableau or Power BI is key at this stage. The entry-level salary for data analysts in India typically ranges from INR 3.2 lakh to INR 4.6 lakh per annum. The entry-level salary for data analysts in the United States typically ranges from $59,528 to $80,131 per year.
Junior Data Analyst / Associate Analyst: After gaining some experience, analysts may take on more complex data sets, work on cross-functional teams, and start contributing to decision-making processes. In the United States, a Junior Data Analyst generally earns around $58,127 per year on average. In contrast, in India, the total compensation for a similar role is approximately ₹4,53,251 per year, with the average salary being around ₹4,33,227 annually.
Senior Data Analyst: At this stage, professionals lead more sophisticated projects, mentor junior analysts, and take responsibility for more strategic, high-impact analyses. Expertise in Python, R, and machine learning techniques can be highly advantageous. The estimated total compensation for a Senior Data Analyst is ₹13,00,000 per year (with an average salary of ₹12,00,000) in India, while in the U.S., it is approximately $1,60,782 per year (with an average salary of $1,18,394).
Data Scientist or Specialist Roles: With continuous learning and experience, data analysts can move into data science, focusing on building predictive models, working with unstructured data, or leveraging machine learning to draw deeper insights. In the U.S., the estimated total annual pay for a Data Scientist is $160,031, with an average salary of $115,033, while in India, the estimated total annual pay is ₹1,380,000, with an average salary of ₹1,200,000.
Leadership Roles (e.g., Analytics Manager or Director of Data): With enough experience, data professionals may transition into management, overseeing data teams, strategy, and analytics-driven decision-making across the organization.
Real-World Applications of Data Analysis
Data analysis has become crucial across industries for driving decision-making, improving efficiency, and fostering innovation. Here are some real-world applications of data analysis across different sectors, highlighted through case studies:
1. Healthcare: Predictive Analytics for Patient Care
- Case Study: Cleveland Clinic & IBM Watson
- Problem: Cleveland Clinic wanted to improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment plans by leveraging data.
- Solution: The clinic partnered with IBM Watson to analyze vast amounts of medical data. Predictive analytics was used to assist physicians in diagnosing patients faster and suggesting personalized treatment options.
- Outcome: By utilizing advanced data analysis tools, the clinic achieved quicker diagnosis and improved patient outcomes, reducing the burden on medical staff while enhancing patient care.
2. Finance: Fraud Detection Using Machine Learning
- Case Study: PayPal’s Fraud Detection System
- Problem: PayPal needed to detect fraudulent transactions to protect users and reduce financial losses.
- Solution: PayPal adopted machine learning algorithms and data analysis techniques to monitor and flag potentially fraudulent activity. Real-time analysis of millions of transactions was conducted to identify irregular patterns.
- Outcome: The system significantly reduced fraud, improving user trust and saving PayPal millions in potential losses. Fraud detection became more accurate, lowering false positives while enhancing transaction security.
3. Transportation & Logistics: Route Optimization
- Case Study: UPS’s ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation) System
- Problem: UPS aimed to cut fuel expenses and enhance the efficiency of their delivery operations.
- Solution: UPS developed ORION, a route optimization system that uses data analysis to identify the most efficient delivery routes based on traffic patterns, distance, and delivery priorities.
- Outcome: ORION saved UPS millions of gallons of fuel annually, cut down on emissions, and reduced delivery time. This demonstrated the effectiveness of data analysis in improving logistics and environmental sustainability.
Refer these articles:
- Data Analyst Course Fee in India
- Data Analyst Course Fee in Bangalore
- Data Analyst Course Fee in Chennai
In today’s competitive landscape, data analytics is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. Businesses leveraging data analysis can make informed decisions that lead to improved outcomes, enhanced customer satisfaction, and sustained growth. The ability to interpret data effectively provides organizations with a strategic edge over competitors.
Mastering the key skills outlined in this blog post can significantly enhance your career as a data analyst. By investing in data analyst courses and pursuing data analyst certifications, you can position yourself for success in this dynamic field. Take the time to assess and develop your skills—your future in data analytics awaits!
DataMites Institute is a leading platform for data science and analytics education, offering a comprehensive Certified Data Analyst Course designed to equip students with the essential skills and knowledge needed to excel in the data analytics field. This course covers various topics, including data visualization, statistical analysis, and data-driven decision-making, ensuring a well-rounded education. DataMites is accredited by esteemed organizations such as IABAC and NASSCOM FutureSkills, which enhances the credibility of its programs and assures students of high-quality training. With industry-relevant curricula and expert instructors, DataMites prepares aspiring analysts for successful careers in data analytics.
