Navigating the Distinctive Paths of Data Architects and Data Engineers
Explore the unique roles and responsibilities of data architects and data engineers, highlighting their contributions to data infrastructure. Understand how they collaborate to build robust, scalable systems.

In the tech world, data is king. This article will explore two key players in managing this valuable asset: Data Architects and Data Engineers. Their roles, often misunderstood or conflated, are crucial in turning vast amounts of data into useful information. We'll unravel the distinct functions and skills of each profession, showing how they're vital in our technology-driven world.
By the end of this article, you'll understand the unique roles of Data Architects and Data Engineers and why they're indispensable in today's data-centric tech landscape.
Roles and Responsibilities
Definition:
- Data Architects: They are like the architects of a building, but for data. They design the big plan for how a company will store, organize, and use its data. Their work makes sure that the right data is in the right place and is easy to use.
- Data Engineers: Think of them as the builders who follow the architect's plan. They build and maintain the systems that handle data based on what the Data Architects have designed. They're the ones who make sure data is collected, stored, and ready for use efficiently and securely.
Responsibilities:
Data Architects:
- System Design: Plan and design data architectures, including databases, data lakes, and warehouses.
- Data Modeling: Create models that define how data is stored, processed, and accessed.
- Strategy & Governance: Develop data strategies and policies to manage data effectively and securely.
Data Engineers:
- Infrastructure Development: Build and maintain the infrastructure for data storage and processing.
- Data Processing: Develop, construct, test, and maintain data pipelines and architectures.
- Performance Optimization: Ensure the data systems are efficient, scalable, and support analytics needs.
These points offer a concise comparison of the key responsibilities of Data Architects and Data Engineers, highlighting the strategic and technical aspects of each role in data management.
Refer these below articles:
- Difference Between Data Scientist and Data Engineer
- Data Engineer Salary in India
- Data Engineer vs Data Analyst
Integrating Roles in the Data Ecosystem
Data Architects are the visionaries. They set the stage by designing data systems and structures that define how data is collected, stored, and accessed. Their role is crucial in establishing the foundation and long-term data strategy for an organization, ensuring scalability and alignment with business goals.
Data Engineers, on the other hand, are the implementers. They take the vision and blueprints created by Data Architects and turn them into reality. They build and maintain the data infrastructure, ensuring that it runs smoothly and efficiently, and adapt it to meet evolving needs and challenges in data processing.
Together, these roles ensure that an organization's data is not only well-organized and accessible but also primed for analysis, insights, and decision-making.
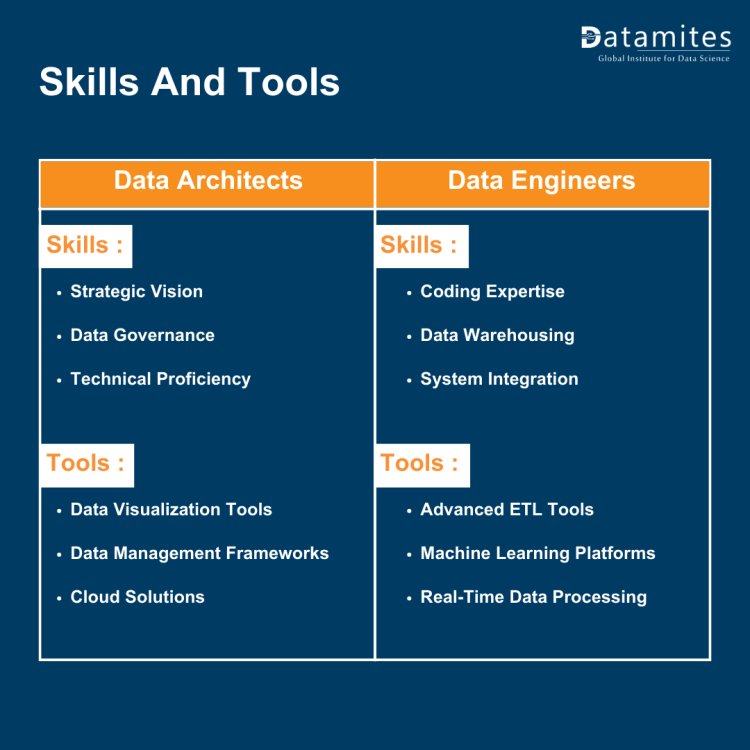
Skills
Data Architects:
- Strategic Vision: Ability to develop long-term data strategies aligned with business objectives.
- Data Governance: Knowledge of data privacy laws and ethical handling of data.
- Technical Proficiency: Understanding of database design, data warehousing, and ETL processes.
Data Engineers:
- Coding Expertise: Proficient in programming languages like Python, SQL, and Java for data manipulation.
- Data Warehousing: Skills in building and managing large-scale data storage solutions.
- System Integration: Ability to integrate disparate data systems for streamlined operations.
Tools
Data Architects:
- Data Visualization Tools: Like Tableau or Power BI for presenting data architectures.
- Data Management Frameworks: Knowledge of frameworks like Apache Kafka for data processing.
- Cloud Solutions: Expertise in cloud-based data solutions like AWS Redshift, Google BigQuery.
Data Engineers:
- Advanced ETL Tools: Such as Apache NiFi, StreamSets for data extraction and transformation.
- Machine Learning Platforms: Familiarity with ML tools like TensorFlow for data-driven insights.
- Real-Time Data Processing: Experience with technologies like Apache Storm or Spark Streaming.
Both Data Architects and Data Engineers must continually update their skill sets and toolkits to stay ahead in the rapidly evolving field of data technology.
Educational Paths
Data Architects:
- Typically hold a bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field.
- Advanced degrees like a master’s in data or computer science can be beneficial.
- Courses in database design, data modeling, and systems analysis are crucial.
Data Engineers:
- Usually have a bachelor’s degree in computer science, engineering, or a similar field.
- Specialized knowledge in software development and database management is often required.
- Hands-on experience with programming and data tools is highly valued.
Specialized Certifications
Data Architects:
- Certified Solution Architect (IBM), Associate Big Data Engineer (DASCA), Google Professional Data Engineer, and Azure Data Engineer Associate (Microsoft) collectively offer a comprehensive skill set for aspiring data architects.
- Continuous learning in emerging technologies and data compliance regulations.
Data Engineers:
- The Certified Data Engineer certification from IABAC, focusing on big data technologies, is particularly valuable.
- Additionally, training in cloud services (AWS, Azure, GCP), machine learning fundamentals, and real-time data processing tools (such as Apache Kafka) are crucial skills for modern data engineers to master, enhancing their ability to manage and analyze large data sets effectively.
Career Paths and Progression
Data Architects:
- Starting Point: Often begin as database administrators or analysts.
- Mid-Career: Progress to senior data architect roles, focusing on larger, more complex data strategies.
- Advanced Roles: Potential to evolve into roles like Chief Data Officer or enterprise architect, influencing organizational data policies and strategies.
Data Engineers:
- Early Career: Typically start as software developers or database administrators.
- Growth Path: Advance to senior data engineer positions, handling larger and more complex data systems. A 2021 DICE study revealed a 50% increase in Data Engineer job postings, more than double the growth for Data Scientists, highlighting a substantial rise in demand for Data Engineering skills.
- Leadership Opportunities: Can progress to roles like Lead Data Engineer, Data Manager, or even CTO, overseeing broader data infrastructure.
Read these below articles:
- How to Become a Data Engineer in India?
- How to Become a Data Engineer in Bangalore?
- How to Become a Data Engineer in Chennai?
Comparison in Seniority and Decision-Making
Data Architects tend to have more strategic, high-level decision-making roles. They set the direction for how data is managed and used across the organization.
Data Engineers, while technically proficient and critical to implementation, usually focus on operational and technical decision-making within the scope defined by the architects.
As both advance, their roles can overlap, with senior engineers involved in strategic decisions and architects in technical choices, reflecting a collaboration essential for effective data management.
Salary
Data Architects: Generally earn higher salaries due to their strategic role and experience requirements. Salaries can range significantly based on location, experience, and company size.
- United States: Data Architects earn an average of $164,639 per year.
- United Kingdom: Average annual salary for Data Architects is £67,371.
- India: Data Architects have an average yearly salary of ₹2,631,877.
- Canada: The annual average salary for Data Architects is CAD 130,840.
- Australia: Data Architects earn an average of AUD 161,500 per year.
- Germany: The average salary for Data Architects is €78,039 in 2023.
- Switzerland: Average annual salary for a Data Architect is CHF 126,016.
- UAE: Data Architects have an average salary of AED 305,209.
- Saudi Arabia: The average salary for Data Architects is SAR 72,500.
- South Africa: Data Architects earn an average salary of ZAR 862,895.

Data Engineers: Also command competitive salaries, especially with skills in emerging technologies. The salary range varies with experience and specialization.
- United States: Data Engineers have an average salary of $126,433 annually.
- United Kingdom: The average yearly salary for Data Engineers is £56,794.
- India: Data Engineers earn about INR ₹845,000 per year on average.
- Canada: The average annual salary for Data Engineers is CAD 102,013.
- Australia: Data Engineers have an average yearly salary of AUD 126,958.
- Germany: The average salary for Data Engineers is €70,033 per year.
- Switzerland: Data Engineers earn an average of CHF 106,199 annually.
- United Arab Emirates: The average salary for Data Engineers is AED 140,914.
- Saudi Arabia: Data Engineers have an average salary of SAR 163,862.
- South Africa: The average annual salary for Data Engineers is ZAR 456,332.

Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Case Study 1: Retail Industry
- Role of Data Architects: Developed a comprehensive data model to integrate customer data across multiple platforms.
- Role of Data Engineers: Implemented a real-time data pipeline for processing customer interactions, enhancing personalized marketing.
- Impact: Boosted sales by 20% through targeted marketing campaigns based on customer data analysis.
Case Study 2: Healthcare Sector
- Data Architects: Designed a secure, compliant data infrastructure for patient records.
- Data Engineers: Built and maintained the data storage system, ensuring fast, reliable access to patient information.
- Outcome: Improved patient care and streamlined operations, reducing wait times by 30%.
Case Study 3: Financial Services
- Data Architects: Created a robust data architecture to handle high-volume trading data.
- Data Engineers: Developed a high-performance data processing system to analyze trading patterns in real-time.
- Result: Enhanced trading strategies, leading to a 15% increase in profitable trades.
Case Study 4: E-Commerce Platform
- Data Architects: Established a scalable data warehouse to store and analyze vast amounts of transaction data.
- Data Engineers: Integrated various data sources into the warehouse, enabling comprehensive business intelligence.
- Success: Achieved a 25% increase in customer retention through improved data-driven decision-making.
Case Study 5: Smart City Initiatives
- Data Architects: Designed the data framework for integrating IoT devices across the city.
- Data Engineers: Implemented the infrastructure to collect and process data from thousands of sensors.
- Advancement: Enhanced city management and services, including traffic flow and public safety improvements.
Also refer these below articles:
- What is the Data Engineer Course Fee in Bangalore?
- How Much is the Data Engineer Course Fee in Pune?
- How Much is the Data Engineer Course Fee in Chennai
These case studies demonstrate the pivotal roles of Data Architects and Data Engineers in various industries, showcasing their ability to drive innovation and efficiency through strategic data management and engineering.
For aspiring professionals, the choice between these paths should align with their interests and strengths. Those drawn to big-picture thinking, strategic planning, and system design may find fulfillment in the role of a Data Architect. In contrast, those who enjoy hands-on technical work, coding, and building tangible solutions may gravitate towards Data Engineering. Both paths offer rewarding careers in a field that is only set to grow in importance and impact. The key is in recognizing where your passions and skills intersect with the needs of this ever-evolving domain.
DataMites plays a pivotal role in shaping future professionals in these fields. Recognizing the growing demand and significance of these roles, DataMites offers a comprehensive Certified Data Engineer Training. This training program, accredited with IABAC and NASSCOM FutureSkills, is designed to equip learners with the necessary skills in data engineering. It delves into essential topics such as big data technologies, cloud services, and real-time data processing, providing a solid foundation for those looking to pursue a career in Data Engineering.
DataMites Training Institute offers a globally recognized Data Engineer Course, designed to equip learners with essential data engineering skills. The course covers Python, Big Data, SQL, Data Wrangling, and Pandas, providing practical training for real-world applications. Accredited by IABAC, it guarantees industry-recognized certification and enhances career prospects. With expert mentorship and job support, DataMites prepares professionals for success in the data-driven industry.





