Climbing the Data Science Ladder - Data Science Levels

Think of data as a big puzzle. At the start, data scientists collect and clean the puzzle pieces to make them fit together. It's like getting ready for a big treasure hunt. Once the pieces are ready, we start looking at the puzzle. First, we see the big picture - like finding shapes in the clouds. Then, we guess what's missing and what might happen next. It's like making predictions about the weather.
But we don't stop there. We want to control the puzzle and make it our own. So, we use what we know to change the puzzle's path, like choosing which way to go on a trip. We'll explore the different levels of data science and see how they help us solve puzzles and make choices. It's a fun journey where we learn new things and have a great time along the way!
The Importance of Data Science: Shaping a Smarter World
At its essence, data science involves the collection, organization, and analysis of data to extract valuable insights and identify patterns. Think of it as a detective meticulously solving mysteries in a data-rich landscape.
Data science holds immense importance because it equips us with the ability to make informed decisions. In the realm of business, it guides companies in understanding their customers, predicting market trends, and crafting products that resonate with the audience. In healthcare, it contributes to improved treatments and early disease detection.
Jobs requiring Data Science Skills are anticipated to surge by 27.9% by 2026, as per the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. This substantial growth underscores the escalating demand for professionals adept in Data Science, affirming its pivotal role in the evolving job market.
Its impact extends to our daily lives as well. Consider how platforms like Netflix recommend movies tailored to your preferences or how GPS navigation systems determine the optimal routes for your journey. These applications are driven by data science.
Refer these below articles:
- A Comprehensive Guide on the Data Science Lifecycle
- What Does a Data Scientist Do?
- Data Scientist Required Skills
Levels of Data Science
1. Junior Data Scientist: Entry-level, focuses on basic data handling and analysis.
Junior Data Scientists are the newcomers to the field, often with a background in statistics, computer science, or a related field. They are tasked with foundational data tasks, such as data cleaning, simple analysis, and generating reports. Their main goals are to learn and gain experience in the data science workflow.
Responsibilities:
- Data collection and cleaning.
- Basic data analysis using tools like Excel.
- Assisting in data visualization.
- Learning fundamental statistics and programming skills.
2. Data Scientist: Intermediate level, with skills in Python, R, SQL, and machine learning.
Data Scientists have a broader skill set and can handle more complex data tasks. They use programming languages like Python and R to build machine learning models, conduct in-depth analysis, and extract valuable insights from data.
Responsibilities:
- Developing and implementing machine learning models.
- Extracting insights and patterns from data.
- Crafting SQL queries for data access and manipulation.
- Collaborating with domain experts to solve business problems.
3. Senior Data Scientist: Advanced level, guiding analytic studies and understanding business aspects.
Senior Data Scientists are experienced professionals who not only excel in data analysis but also possess a deep understanding of the business context. They take a leading role in shaping data strategies, defining objectives, and guiding analytic studies.
Responsibilities:
- Leading complex data projects.
- Defining business objectives for data analysis.
- Mentoring and guiding junior team members.
- Collaborating with stakeholders to align data efforts with business goals.
4. Principal Data Scientist: Top level, leading data strategy and possessing strong leadership abilities.
Principal Data Scientists are the highest-ranking experts in the field. They have a comprehensive understanding of data science, machine learning, and business strategy. They play a pivotal role in shaping the organization's data strategy, making critical decisions, and providing leadership to the entire data science team.
Responsibilities:
- Setting the overall data strategy for the organization.
- Making high-level decisions on data infrastructure and technology.
- Serving as a visionary leader in the data science field.
- Collaborating with top executives to ensure data-driven decision-making at the highest level.
In the evolving world of data science, professionals progress through these levels by acquiring data science skills, gaining experience, and demonstrating their ability to deliver value through data-driven insights. Each level brings its own set of challenges and opportunities, contributing to the growth and success of data-driven organizations.
Skill Development at Each Level:
1. Junior Data Scientist:
- Programming Skills: Learn basic programming languages like Python and R.
- Data Handling: Gain proficiency in data cleaning and preprocessing techniques.
- Statistics: Develop a foundational understanding of statistics and hypothesis testing.
- Data Visualization: Learn data visualization tools like Matplotlib or ggplot2.
- Tools: Familiarize yourself with tools like Excel and basic SQL.
2. Data Scientist:
- Advanced Programming: Enhance your programming skills in Python and R for data manipulation and analysis.
- Machine Learning: Gain expertise in machine learning algorithms and libraries (e.g., scikit-learn, TensorFlow, or PyTorch).
- Database Management: Master SQL for querying and managing databases.
- Data Visualization: Become proficient in creating interactive and informative data visualizations.
- Domain Knowledge: Develop domain-specific knowledge relevant to your industry.
3. Senior Data Scientist:
- Advanced Machine Learning: Deepen your understanding of machine learning and explore advanced techniques.
- Business Acumen: Develop a strong understanding of your organization's industry, objectives, and challenges.
- Project Leadership: Hone your project management skills and lead complex data projects.
- Communication: Improve your ability to communicate complex findings to non-technical stakeholders.
- Mentorship: Begin mentoring junior team members and sharing your knowledge.
4. Principal Data Scientist:
- Data Strategy: Shape and execute the organization's data strategy.
- Leadership: Exhibit strong leadership and strategic thinking abilities.
- Innovation: Drive innovation through the application of cutting-edge data science techniques.
- Executive Communication: Communicate effectively with top-level executives, translating data insights into strategic decisions.
- Ethics and Compliance: Ensure data practices align with ethical and legal standards.
Read these below articles:
- Data Science Career Scope in Bangalore
- Data Science Career Scope in Chennai
- Data Science Career Scope in Pune
Career Progression:
Junior Data Scientist to Data Scientist: To progress from a junior to a data scientist, focus on expanding your technical skills, such as machine learning and data analysis. Collaborate on real-world projects to gain experience and build a portfolio. Seek out mentors for guidance.
Data Scientist to Senior Data Scientist: Transitioning to a senior role requires not only technical expertise but also strong business acumen. Lead projects, demonstrate the ability to solve complex problems, and mentor junior team members. Effective communication and project management skills become crucial.
Senior Data Scientist to Principal Data Scientist: As a senior data scientist, aim to shape the organization's data strategy. Foster innovation and develop executive-level communication skills. Establish yourself as a thought leader within the field and ensure data practices align with ethical and compliance standards.
Overall, career progression in data science is a journey of continuous learning, practical experience, and the ability to adapt to evolving technologies and business needs. It's essential to stay curious, embrace challenges, and seek opportunities for growth at each career level.
Challenges and Opportunities at Each Level
1. Junior Data Scientist:
Challenges:
- Limited Experience: Lack of real-world experience can be a hindrance when tackling complex data problems.
- Skill Development: The challenge lies in acquiring and honing foundational skills in programming and statistics.
- Scope of Projects: Junior data scientists often work on smaller, less complex projects.
Opportunities:
- Learning: This stage is an excellent opportunity to learn and gain practical experience.
- Mentorship: Junior data scientists can benefit from mentorship by more experienced colleagues.
- Skill Building: Building a strong foundation in data handling and analysis opens the door to future growth.

2. Data Scientist:
Challenges:
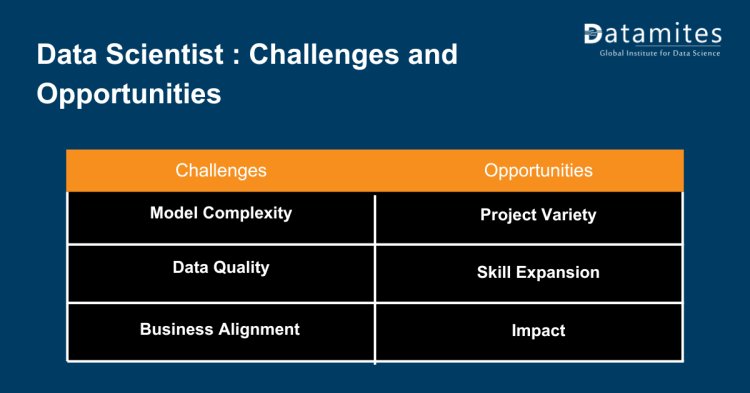
- Model Complexity: Working on more advanced projects introduces challenges related to complex machine learning models.
- Data Quality: Handling large datasets and ensuring data quality can be demanding.
- Business Alignment: Balancing technical work with understanding business goals becomes crucial.
Opportunities:
- Project Variety: Data scientists work on a wider range of projects, gaining exposure to diverse domains.
- Skill Expansion: Opportunities to delve deeper into machine learning and advanced analytics arise.
- Impact: The chance to make a substantial impact on the organization's success increases.
3. Senior Data Scientist:
Challenges:
- Leadership Expectations: As senior data scientists take on leadership roles, there's increased pressure to guide teams and make strategic decisions.
- Communication: Effective communication with non-technical stakeholders becomes paramount.
- Innovation: Staying at the forefront of rapidly evolving technologies can be challenging.
Opportunities:
- Leadership: Senior data scientists can lead and shape high-impact projects, influencing the organization's direction.
- Mentorship: Opportunities to mentor junior colleagues and share knowledge arise.
- Strategic Impact: A chance to contribute to the organization's long-term data strategy and innovation efforts.

4. Principal Data Scientist:
Challenges:
- High Expectations: Expectations are significantly higher, with responsibility for shaping the organization's data strategy.
- Ethical Considerations: Ensuring ethical and compliant data practices can be complex.
- Innovation and Risk: Balancing innovation with risk management is a key challenge.
Opportunities:
- Data Strategy: Principals have the opportunity to set the data strategy for the entire organization.
- Thought Leadership: Establishing oneself as a thought leader in the field.
- Executive Influence: The ability to influence executive decisions through data-driven insights and strategies.

Also refer these below articles:
- What would be the Data Science Course Fee in India?
- Data Science Course Fee in Chennai
- Data Science Course Fee in Bangalore
At each career level in data science, professionals face unique challenges and opportunities. These challenges provide opportunities for growth, learning, and career advancement, while the opportunities allow data scientists to make a significant impact on their organizations and the field of data science as a whole.
In the realm of data science, a career path unfolds as a journey filled with growth and adaptability. Beginning as a Junior Data Scientist, individuals build a strong foundation and gain hands-on experience. As they progress to Data Scientist Roles, they expand their skill set and tackle more intricate challenges. The transition to Senior Data Scientist brings leadership opportunities, strategic thinking, and a deeper connection with business objectives. Finally, as Principal Data Scientists, they shape data strategies, drive innovation, and wield influence at the highest levels.
What makes data science captivating is its ever-evolving nature, with emerging technologies and novel complexities. Success in this field requires continuous learning and an openness to change. Ultimately, a career in data science offers not just professional development but also the chance to contribute significantly to the data-driven transformation of industries, making it a journey filled with potential and lasting impact.