Generative AI and Predictive AI: Key Differences Explained
Discover the key differences between Generative AI and Predictive AI, exploring their functions, methodologies, and roles in shaping the future of artificial intelligence.
Artificial Intelligence has emerged as one of the most transformative technologies of the 21st century. From virtual assistants that answer your questions to algorithms that predict stock market trends, AI is shaping the way industries operate and individuals interact with technology. Among the many branches of AI, two of the most prominent are Generative AI and Predictive AI.
Although they are often mentioned together, their roles, capabilities, and applications differ significantly. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses, professionals, and learners whether you’re building new solutions or exploring an artificial intelligence course to upskill.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into what Generative AI and Predictive AI are, highlight their key differences, and explore real-world applications along with their advantages and limitations.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a subset of artificial intelligence focused on creating new content. Unlike traditional models that only analyze data, generative AI models learn patterns and structures from existing datasets and then produce entirely new outputs that resemble human-created work.
At its core, generative AI relies heavily on neural networks and deep learning techniques, including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and large language models (LLMs). These models are trained on massive amounts of text, images, or audio and then generate new results based on the learned patterns.
Examples of Generative AI:
- Text generation: ChatGPT creating articles, stories, or code.
- Image generation: Tools like DALL·E or MidJourney producing realistic images.
- Music and art: AI composing melodies or designing artworks.
- Healthcare innovation: Generating synthetic medical data to train diagnostic tools.
Generative AI excels in creativity-driven applications, where the objective is not to forecast future events but to generate entirely new and original outputs. According to a report by Markets and Markets, the global Generative AI market is on a rapid growth path expected to expand from USD 71.36 billion in 2025 to USD 890.59 billion by 2032, registering an impressive CAGR of 43.4% during the forecast period.
What is Predictive AI?
Predictive AI, on the other hand, is focused on forecasting outcomes based on historical data. Instead of creating new content, it analyzes existing datasets to identify patterns and make informed predictions about future events.
The foundation of predictive AI lies in machine learning models, including regression, classification, and time-series forecasting. These models use past and present data to make accurate projections that help organizations in planning and decision-making.
Examples of Predictive AI:
- Business forecasting: Predicting sales trends for the upcoming quarter.
- Healthcare analytics: Estimating the likelihood of patient readmissions.
- Finance: Stock price predictions or fraud detection in banking.
- Retail: Forecasting customer demand and inventory management.
Predictive AI empowers businesses to minimize risks, enhance operational efficiency, and make smarter, data-driven decisions with greater confidence. Leveraging advanced algorithms, Predictive AI can identify fraudulent transactions with up to 99% accuracy, providing organizations with a powerful tool for security and trust.
Refer these below articles:
- Why Artificial Intelligence Matters More Than Ever
- How Artificial Intelligence is Transforming Digital Marketing
- What is a Convolutional Neural Network?
Generative AI vs. Predictive AI: Understanding the Key Differences
Although both Generative AI and Predictive AI are based on machine learning principles, their objectives, outputs, and use cases differ significantly. Here’s a detailed comparison:
1. Primary Function
- Generative AI: Generative AI is designed to create original and novel content, simulating human-like creativity. Unlike conventional AI that works only with existing data, Generative AI can produce new outputs that have never existed before. Examples include writing articles, designing graphics, or generating molecules for research.
- Predictive AI: Predictive AI is focused on forecasting future outcomes using historical data. It does not generate new content but provides insights and predictions about trends, probabilities, or risks, enabling businesses and individuals to make informed decisions.
2. Output Type
- Generative AI: The output of Generative AI is creative and innovative. It can generate text, images, music, videos, product prototypes, or realistic 3D models. Tools like ChatGPT can draft engaging text, while image-generation models like DALL·E create unique visual content from prompts.
- Predictive AI: Predictive AI produces information-driven, decision-oriented outputs. This includes forecasts, probability scores, risk assessments, and recommendations. For instance, it can predict customer behavior, future sales, or potential system failures.
3. Core Technology
- Generative AI: Generative AI relies on advanced deep learning models such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), transformer architectures (like GPT), and diffusion models. These allow the AI to learn complex patterns and produce outputs that appear highly human-like or original.
- Predictive AI: Predictive AI often uses traditional machine learning techniques like regression, classification algorithms, and time-series analysis. These models are optimized to detect correlations, identify patterns, and make accurate predictions rather than creating new data.
4. Learning Approach
- Generative AI: Generative AI learns by understanding and modeling the underlying structure of data, enabling it to create content that is both coherent and contextually relevant. It often requires large datasets and extensive training to generate high-quality outputs.
- Predictive AI: Predictive AI learns from historical trends and patterns to forecast future outcomes. Its focus is on accuracy and reliability, and it continually updates predictions as new data becomes available, improving its decision-making over time.
According to ABI Research, the Artificial Intelligence software market was valued at US$122 billion in 2024. With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25%, the market is projected to expand significantly, reaching US$467 billion by 2030.
Read these below articles:
Practical Applications in Real-World Scenarios
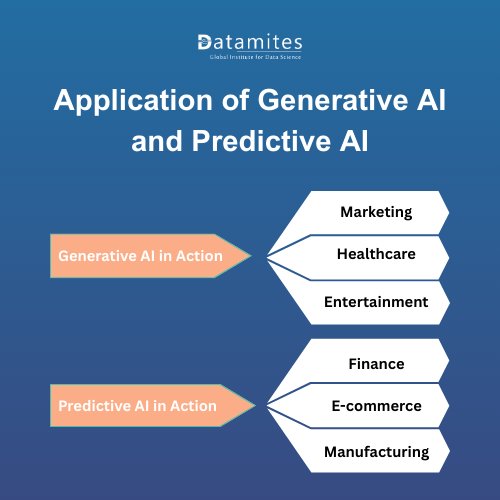
Generative AI in Action
- Marketing: Generative AI enables automated ad copywriting, personalized emails, and campaign content creation. AI-driven personalization in marketing can boost revenue by 10–20% and significantly enhance customer engagement.
- Healthcare: Generative AI plays a critical role in drug molecule generation and creating synthetic medical data for research and training. AI in healthcare could deliver up to USD 150 billion in annual savings for the U.S. healthcare economy by 2026.
- Entertainment: From AI-generated music and art to automated scriptwriting, generative models are transforming the entertainment industry. The global Generative AI market will surge from USD 71.36 billion in 2025 to USD 890.59 billion by 2032, growing at a remarkable CAGR of 43.4%.
Predictive AI in Action
- Finance: Predictive AI is widely applied in credit risk scoring, fraud detection, and stock market forecasting. AI-powered fraud detection systems are expected to save banks over USD 10 billion annually by 2027.
- E-commerce: Online platforms use Predictive AI for personalized recommendations and dynamic pricing strategies. Those recommendation engines powered by predictive analytics account for up to 35% of Amazon’s total revenue.
- Manufacturing: Predictive AI supports predictive maintenance by analyzing machine performance and preventing breakdowns. That predictive maintenance can reduce downtime by 30–50% and extend equipment life by 20–40%.
Generative AI and Predictive AI represent two distinct yet complementary aspects of artificial intelligence. Generative AI focuses on creation and innovation, while Predictive AI emphasizes analysis and forecasting. Together, they are reshaping industries, driving efficiency, and opening new possibilities for businesses and individuals alike.
Artificial Intelligence Course in Ahmedabad is opening new opportunities across diverse sectors. Businesses are increasingly adopting AI solutions for smarter data-driven decision-making, accurate trend forecasting, and seamless process automation. In agriculture, AI-powered tools are transforming practices through crop monitoring, early disease detection, and precise weather prediction. As a result, Ahmedabad is rapidly evolving into a hub of innovation and efficiency, with AI driving technological advancement, improving quality of life, and fueling economic growth.
The Artificial Intelligence Course in Coimbatore offered by DataMites is a comprehensive training program designed to equip learners with the essential skills and knowledge needed to thrive in the rapidly expanding AI industry. The course is structured to cater to both beginners and experienced professionals, providing flexible learning options that include online classes, offline classes, and self-learning. Accredited by globally recognized bodies such as IABAC and NASSCOM FutureSkills, the certification adds significant value to the learner's professional credentials, enhancing career prospects in the field of Artificial Intelligence.
