Guide to Data Engineer Career
A Data Engineer designs, builds, and maintains systems that allow organizations to process and analyze data efficiently. This career involves working with databases, pipelines, and big data technologies to support data-driven decision-making.

In an era where data is likened to the new oil, the mastery of managing, processing, and utilizing this invaluable resource has become crucial for businesses and organizations worldwide. This is where the field of Data Engineering and its practitioners, Data Engineers, play a pivotal role.
We aim to lay down a detailed groundwork for those aspiring to embark on a career as a Data Engineer. From understanding the fundamental concepts of the field to exploring the skills and qualifications needed, the various roles and responsibilities you might undertake, and the career pathways available, we will cover every aspect you need to know to kickstart your journey in this dynamic and rewarding field.
What is Data Engineering?
Data Engineering is a crucial branch of the broader field of data science, primarily focused on the practical application of data collection, management, and optimization. It involves developing and maintaining robust infrastructure and systems that facilitate the efficient processing, storage, and analysis of large sets of data. This field blends various disciplines, including software engineering, database architecture, and big data analytics, to ensure that data flows seamlessly and is readily accessible for insightful analysis.
The Evolution of Data Engineering in the Digital Age
The digital age has seen an exponential growth in data volume, velocity, and variety, leading to the evolution of Data Engineering from its rudimentary form of database management to a sophisticated discipline. This evolution was propelled by the advent of big data technologies, cloud computing, and advanced analytics.
The Big Data Infrastructure Market is anticipated to achieve a valuation of $4.2 billion by the year 2026, demonstrating a remarkable compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.3% from 2021 to 2026. This substantial growth is attributed to the swift advancements in consumer and machine data, driving the demand for robust infrastructure in the industry. This forecast is provided by Industry Arc.
The role of Data Engineers has shifted from merely managing data to architecting complex systems that can handle the scale and complexity of modern data ecosystems. This transformation has been pivotal in enabling organizations to capitalize on the data deluge, driving innovations in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and predictive analytics.
Refer these below articles:
- Data Engineer Salary in India
- Navigating the Distinctive Paths of Data Architects and Data Engineers
- Difference Between Data Scientist and Data Engineer
Role and Importance in Today's World
1. Key Contributions to Data-Driven Decision Making
Data Engineers play a pivotal role in the forefront of transforming raw data into a valuable resource. These professionals are instrumental in designing intricate data pipelines that supply analytical tools and algorithms with the necessary information. Their primary focus is on ensuring data accuracy, consistency, and timeliness. Through their dedicated work, organizations can effectively harness the power of data analytics, leading to a paradigm shift in decision-making. This shift, from intuition-based to data-driven decision-making, has sparked a revolution in how businesses strategize, operate, and compete.
Amid this evolving landscape, Statista's projections highlight a significant surge in the global datasphere's real-time data volume between 2023 and 2025. Anticipated to nearly double, the data size is expected to rise from 25 zettabytes to an impressive level. This exponential growth underscores the increasing importance of skilled Data Engineers in managing and leveraging this massive influx of data.
2. Impact on Business Insights and Strategy
Data Engineers play a pivotal role in extracting actionable insights from data, which are instrumental in shaping business strategies. By ensuring the availability and integrity of data, they empower business leaders and analysts to uncover trends, predict market dynamics, and make informed strategic decisions. Their contribution is vital in optimizing operations, enhancing customer experiences, and driving growth. In essence, Data Engineers are the unsung heroes in the background, fueling the data-driven strategies that shape the competitive landscape of businesses across various industries.
Roles and Responsibilities of Data Engineers
1. Designing and Maintaining Data Pipelines
Purpose: Ensuring a seamless flow of data from its origin to its analytical destinations.
Key Tasks:
- Developing and optimizing ETL processes.
- Implementing pipelines that are efficient, scalable, and resilient to errors.
- Continuous monitoring and maintenance to adapt to evolving data needs.
2. Managing and Optimizing Data Storage and Retrieval
Purpose: Selecting and administering the right storage solutions to meet organizational needs.
Key Tasks:
- Ensuring data integrity and security.
- Enhancing performance for rapid data access.
- Balancing cost-effectiveness with performance requirements.
3. Data Architecture Design
Purpose: Structuring the architecture of data storage systems to support the specific requirements of various data types and use cases.
Key Tasks:
- Designing logical and physical data models that cater to both current and future needs.
- Creating a scalable architecture that supports growing data volumes and complexity.
- Ensuring that the data architecture aligns with the overall business strategy and objectives, allowing for seamless integration and utilization across different departments.
4. Performance Tuning and Optimization
Purpose: Enhancing the efficiency of data storage and retrieval processes to maximize system performance.
Key Tasks:
- Regularly assessing and optimizing database performance using various tuning techniques.
- Identifying and resolving bottlenecks in the data storage and retrieval processes.
- Implementing best practices in indexing, query optimization, and data partitioning to ensure swift and efficient access to data, especially in high-demand environments.
Read these below articles:
- How to Become a Data Engineer in India?
- How to Become a Data Engineer in Bangalore?
- How to Become a Data Engineer in Chennai?
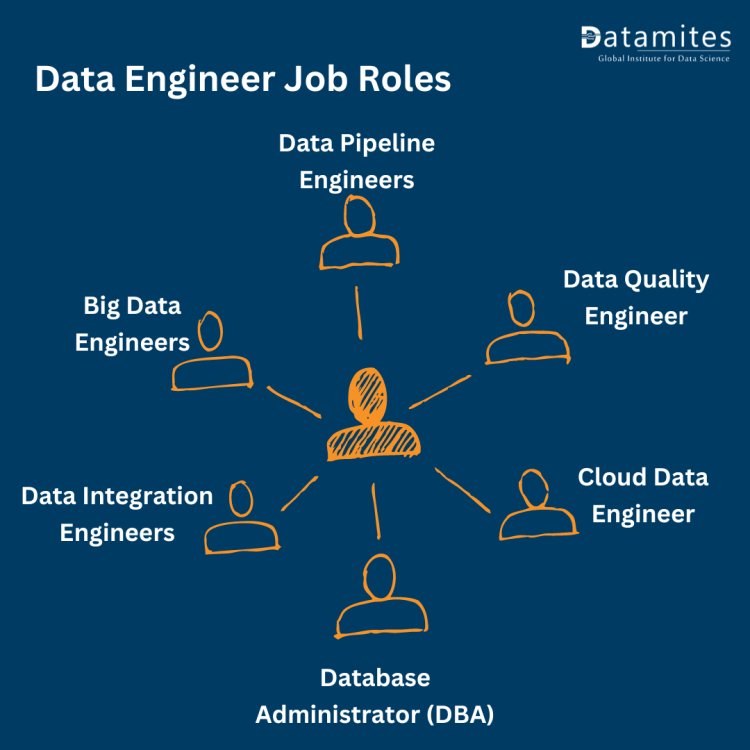
Specialized Data Engineer Job Roles
A variety of specialized roles have emerged to address the diverse challenges and requirements of handling big data. These data engineer job roles are tailored to specific aspects of data management and processing, reflecting the depth and breadth of expertise required in this ever-evolving domain. From designing intricate data pipelines to ensuring data quality and security in cloud-based systems, each role contributes uniquely to the overall effectiveness and efficiency of data-driven operations in organizations.
Let's explore some of these data engineer jobs and their contributions to the field of Data Engineering.
1. Data Pipeline Engineers
Purpose: Building and managing the infrastructure for automated data flow.
Key Tasks:
- Designing pipelines to handle various data formats and large volumes.
- Integrating different data processing frameworks.
- Ensuring high throughput and low latency in data processing.
2. Big Data Engineers
Purpose: Tackling the challenges of massive data sets that exceed traditional database capabilities.
Key Tasks:
- Implementing big data technologies like Hadoop, Spark, and NoSQL.
- Facilitating advanced data analysis and predictive modeling.
- Ensuring scalability and efficiency in big data solutions.
3. Data Integration Engineers
Purpose: Merging data from diverse sources into a unified system.
Key Tasks:
- Employing ETL tools and techniques for effective data amalgamation.
- Ensuring consistency and accessibility of integrated data.
- Facilitating comprehensive analytics and reporting by providing a holistic data view.
4. Database Administrator (DBA)
Purpose: Managing, overseeing, and maintaining a company's database systems.
Key Tasks:
- Ensuring the databases are available, reliable, and secure.
- Performing regular database maintenance tasks such as backups, tuning, and troubleshooting.
- Collaborating with Data Engineers and Developers to optimize database performance and schema design.
5. Cloud Data Engineer
Purpose: Specializing in designing, building, and managing cloud-based data solutions.
Key Tasks:
- Implementing and maintaining cloud data services (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).
- Integrating cloud storage and computing resources with on-premise data systems.
- Ensuring data security and compliance with regulations in cloud environments.
6. Data Quality Engineer
Purpose: Ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of data in business systems.
Key Tasks:
- Developing and implementing data quality standards and processes.
- Identifying, analyzing, and rectifying data quality issues.
- Collaborating with data stakeholders to understand data requirements and improve data quality.
Each of these roles plays a crucial part in the broader landscape of Data Engineering, addressing specific needs and challenges associated with managing, processing, and utilizing data in various environments. These roles are essential in ensuring that data systems are not only technologically advanced but also reliable, secure, and effective in meeting the strategic objectives of organizations.
Educational Qualifications for Data Engineers
The journey to becoming a Data Engineer typically begins with a solid educational foundation in fields related to computing and data. Here are the key educational qualifications that are often essential for a career in Data Engineering:
Degrees
- Bachelor’s and/or Master’s degree in Computer Science, Information Technology, Software Engineering, or related fields.
- Specialized degrees focusing on Data Science, Big Data Analytics, or Data Engineering can be particularly beneficial.
Specializations
- Coursework or specialization in areas like database management, data structures, algorithms, and system design.
- Electives or focused modules in big data technologies, cloud computing, and machine learning.
The Role of Certifications
- Data Engineer Certifications can complement formal education and demonstrate proficiency in specific technologies or tools relevant to Data Engineering (e.g., Hadoop, Spark, AWS, Azure).
- Continuous certification courses help in staying updated with the latest trends and technologies in the field.
Importance of Continuous Learning
- The field of Data Engineering is constantly evolving; hence, continuous learning through online data engineer courses, workshops, and seminars is crucial.
- Engagement in tech communities, attending webinars, and participating in hackathons can also enhance learning and skills development.
Essential Skills for Data Engineers
To excel in the field of Data Engineering, a crucial blend of technical and soft skills, data engineer skills to be exact, is indispensable. These proficiencies empower Data Engineers to adeptly design, implement, and manage data solutions, playing a pivotal role in the dynamic and evolving landscape of data management.
1. Technical Proficiencies
- Programming Languages: Proficiency in languages like Python, Java, Scala, and SQL is crucial for scripting, data manipulation, and database interaction.
- Big Data Tools: Knowledge of big data processing tools and ecosystems, such as Apache Hadoop, Spark, and Kafka.
- Cloud Computing Platforms: Familiarity with cloud services like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform for managing cloud-based data solutions.
2. Soft Skills
- Communication: Ability to clearly articulate technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders and collaborate effectively with teams.
- Problem-Solving: Aptitude for troubleshooting and solving complex data-related issues.
- Teamwork: Working cohesively with cross-functional teams, including data scientists, analysts, and IT professionals.
Combining these educational qualifications and data engineer skills prepares aspiring Data Engineers to tackle the challenges of the field and contribute significantly to their organizations' data infrastructure and strategy.
Career Pathways in Data Engineering
Navigating the career paths in data engineering involves understanding the educational routes, recognizing career progression stages, and being aware of the daily responsibilities and challenges faced in this field. Let’s delve into these aspects to provide a roadmap for aspiring Data Engineers.
1. Educational and Training Pathways
a) Formal Education vs. Self-Learning
- Formal Education: Typically involves obtaining a degree in computer science, data science, or a related field. This path offers a structured curriculum, covering a range of topics from basic programming to advanced data management.
- Self-Learning: Involves utilizing online resources, tutorials, and courses. It's a flexible approach that allows individuals to tailor their learning to specific interests or needs in Data Engineering.
- Blending Both Approaches: Many successful Data Engineers combine formal education with self-directed learning to stay updated with the latest technologies and methodologies in the field.
b) Importance of Hands-On Experience
- Practical Projects: Engaging in real-world projects, either independently or through data engineer internships, helps solidify theoretical knowledge and develop practical skills.
- Contributing to Open Source Projects: Participating in open source projects can provide valuable experience in collaborative development and expose individuals to diverse aspects of Data Engineering.
- Hackathons and Competitions: These platforms offer opportunities to solve real-life problems, encouraging innovative thinking and practical application of skills.
2. Career Progression
a) Junior to Senior-Level Roles
- Entry-Level Positions: Often titled as Junior Data Engineers, focusing on basic data processing and pipeline maintenance.
- Mid-Level Roles: These roles involve more complex responsibilities including designing data models, developing advanced ETL processes, and managing larger-scale data systems.
- Senior-Level Positions: Senior Data Engineers or Data Engineering Managers lead teams, strategize data infrastructure, and make critical decisions regarding tools, technologies, and methodologies.
b) Variations in Roles Across Industries
- Different Sectors: The role of a Data Engineer can vary significantly across industries like finance, healthcare, technology, and retail.
- Tailored Skills and Knowledge: Each industry may require specialized knowledge, for example, financial data security in banking or real-time data processing in e-commerce.
3. Day-to-Day Activities and Challenges
a) Real-World Scenarios and Problem Solving
- Routine Tasks: Includes monitoring data pipelines, troubleshooting issues, updating systems, and optimizing performance.
- Project-Based Work: Involves designing and implementing new data solutions to meet specific business needs or objectives.
- Staying Agile: Data Engineers must adapt to rapidly changing technologies and data landscapes, often requiring quick problem-solving and learning new skills.
Compensation and Job Market Insights in Data Engineering
1. Salary Expectations
Data Engineering stands as a rapidly growing field with a robust job market and competitive compensation, emphasizing the significance of understanding data engineer salaries and job market dynamics globally.
Average Data Engineer Salaries Around the World
- United States: Data Engineers earn an average salary of $124,951 per year (Source: Glassdoor).
- United Kingdom: The average annual salary for a Data Engineer is £56,199 (Source: Indeed).
- India: In India, Data Engineers have an average annual salary of ₹9,99,315 (Source: PayScale).
- Canada: Canadian Data Engineers earn around $101,296 per year on average (Source: Glassdoor).
- Australia: The average annual compensation for a Data Engineer in Australia is AUD 127,143 (Source: Glassdoor).
- Germany: In Germany, Data Engineers make an average of €70,059 per year (Source: Glassdoor).
- Switzerland: The average salary for a Data Engineer is CHF 106,565 per year (Source: Glassdoor).
- UAE: Data Engineers in the UAE earn an average of AED 196,350 annually (Source: Glassdoor).
- Saudi Arabia: In Saudi Arabia, the average annual salary for a Data Engineer is SAR 163,862 (Source: PayScale).
- South Africa: Data Engineers in South Africa earn an average of ZAR 454,536 per year (Source: PayScale).
Factors Influencing Compensation
- Experience Level: Generally, more experienced engineers command higher salaries.
- Skill Set: Specialized skills in big data technologies, cloud platforms, and machine learning can boost compensation.
- Company Size and Sector: Compensation can vary significantly based on the employer's size and the industry sector.
Industry and Geographical Variations
- Tech vs. Non-Tech Industries: Tech companies often offer higher salaries compared to non-tech sectors.
- Location: Salaries can vary widely depending on the cost of living and demand for Data Engineers in specific regions.
2. Job Market Analysis
Demand in Different Sectors
- Diverse Industries: High demand in sectors like technology, finance, healthcare, and retail.
- Role Variations: Demand for various specializations within Data Engineering, such as Big Data, Cloud Engineering, and Data Integration.
Global Opportunities and Challenges
- Worldwide Opportunities: Growing opportunities in both developed and emerging markets.
- Remote Work and Global Teams: Increased remote work options are expanding global job opportunities for Data Engineers.
- Skills Gap: The rapid evolution of technology leads to a skills gap, which can be both a challenge and an opportunity for continuous learning and specialization.

Becoming a Data Engineer: A Step-by-Step Guide
Embarking on a career as a Data Engineer involves a series of strategic steps, from acquiring foundational knowledge to gaining hands-on experience and showcasing your skills. This guide outlines a structured approach to help you navigate this journey.
1. Foundational Knowledge and Skills
- Learn Key Concepts: Start with understanding the basics of data structures, algorithms, and database management.
- Master Programming Languages: Gain proficiency in languages essential for Data Engineering, such as Python, SQL, Java, and Scala.
- Familiarize with Data Tools and Platforms: Get hands-on experience with big data tools (like Hadoop, Spark) and cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).
- Study Data Pipeline and ETL Processes: Learn how to design and manage data pipelines, and understand ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes.
2. Gaining Practical Experience
- Internships: Apply for internships in companies that offer roles in data management, data analysis, or related fields.
- Engage in Project-Based Learning: Work on real-world projects, either independently or as part of online courses, to apply your theoretical knowledge.
- Build a Network: Attend industry conferences, seminars, and meetups to connect with professionals and learn about the latest industry trends.
3. Building a Professional Portfolio
- Create a Portfolio of Your Work: Compile your projects, code samples, and any relevant work that demonstrates your skills and understanding of Data Engineering.
- Maintain an Active GitHub Profile: Regularly update your GitHub repository with your projects and contributions to showcase your coding and collaboration skills.
- Develop an Online Presence: Create a LinkedIn profile highlighting your skills, experience, and projects. Engage with the Data Engineering community online through blogs, forums, or social media.
- Prepare for Interviews: Gain familiarity with the types of technical and problem-solving questions asked in Data Engineering interviews. Practice explaining your projects and how they demonstrate relevant skills.
4. Taking up Certifications and Courses:
- Enroll in reputable online courses or certification programs offered by platforms like DataMites focusing on data engineering topics, big data technologies, or cloud platforms.
- Participate in workshops or bootcamps that provide hands-on experience with specific tools and technologies relevant to data engineering.
Also refer these below articles:
- What is the Data Engineer Course Fee in Bangalore?
- How Much is the Data Engineer Course Fee in Pune?
- How Much is the Data Engineer Course Fee in Chennai
The journey to becoming a Data Engineer is both challenging and rewarding. Key takeaways for aspiring engineers include the importance of a strong foundation in technical skills, the necessity of hands-on experience, and the value of a professional portfolio. This field requires a commitment to continuous learning and adaptation to evolving technologies. Aspiring Data Engineers should be encouraged by the dynamic nature of the field, which offers diverse career opportunities and the ability to make a significant impact in the data-driven world. The future of data engineering is bright, filled with potential for innovation, growth, and a lasting career in a pivotal sector of the tech industry.
DataMites Institute, a premier global institution for data science and artificial intelligence, introduces the Certified Data Engineer Course. This comprehensive program is designed to empower students with advanced skills in data engineering, covering essential aspects such as data processing, storage, and integration. The course concludes with an IABAC certification, endorsing participants as qualified data engineering professionals ready to excel in today's technology-driven landscape.
DataMites provides a Certified Data Engineer Course, a comprehensive and industry-oriented AI program with EU Framework Certification from IABAC. The course covers essential topics in data engineering, including Python, Statistics, Database Fundamentals, Big Data, Data Wrangling, Numpy, Pandas, and more. With the increasing significance of data, the demand for proficient Data Engineers is on the rise, making this certification an excellent opportunity for career growth.





