Guide to Data Science Career

Data science is at the forefront of shaping the future of business and technology. Its growing importance across diverse industries stems from the ability to analyze large sets of data, transforming them into actionable insights. This surge in demand is linked to the digital age, where data is a critical asset for decision-making and problem-solving.
Data scientists, with their expertise in statistical analysis, machine learning, and predictive modeling, are essential in interpreting complex data, helping organizations make informed decisions. Their role extends beyond technical skills, encompassing the understanding of business contexts and challenges. As industries increasingly rely on data-driven strategies, the career in data science is not just promising but is pivotal in steering the future direction of businesses and technological innovation.
The Data Scientist Role
Data scientists play a crucial role in bridging the gap between complex data and actionable business strategies. Their primary responsibility involves translating intricate business cases into clear analytics agendas. This process starts with a deep understanding of the business problem at hand, followed by developing relevant hypotheses. They dive into vast pools of data, identifying patterns and correlations that might go unnoticed by the untrained eye. This task is not just about handling numbers; it involves a nuanced understanding of the business environment to ensure that the data analysis is relevant and actionable.
The data science platforms market exhibited substantial growth, reaching a valuation of $25.7 billion in 2018. Projections indicate a remarkable trajectory, with an expected revenue surge to $224.3 billion by 2026. This impressive expansion is forecasted at a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 31.1%, as per comprehensive research by Research Dive.
The role of data scientists also heavily relies on the use of algorithms. These are not just tools for analysis but are the backbone of making sense of unstructured data. Algorithms help in identifying trends, predicting outcomes, and providing insights that drive decision-making. This aspect of data science requires a robust understanding of machine learning, statistical modeling, and data mining.
Senior data scientists take these responsibilities a step further. They are visionaries who anticipate future business needs, identifying emerging trends and potential challenges. Their expertise is not limited to analysis but extends to crafting solutions for complex business problems. They play a pivotal role in decision-making processes, offering insights that shape business strategy and drive innovation. By leveraging their extensive experience and deep understanding of both data and the business landscape, senior data scientists ensure that organizations are not just reacting to current trends but are also well-prepared for future challenges.
Refer these below articles:
- A Comprehensive Guide on the Data Science Lifecycle
- What Does a Data Scientist Do?
- Data Scientist Required Skills
Data Science Job Market Insights
LinkedIn currently features an impressive 523,000+ data scientist job opportunities worldwide, showcasing the robust demand for skilled professionals in this dynamic field. This vast array of positions spans diverse industries, offering exciting career prospects for individuals with expertise in data science. As organizations globally recognize the strategic importance of data-driven decision-making, the abundance of job listings on LinkedIn highlights the universal appeal and growth potential within the thriving field of data science.
The buoyant data science job market reflects this sector's vitality, witnessing a notable uptick in demand for professionals adept at unraveling intricate data and distilling meaningful insights. This surge is propelled by an escalating dependence on data-driven decision-making across diverse industries, such as technology, healthcare, finance, and retail.
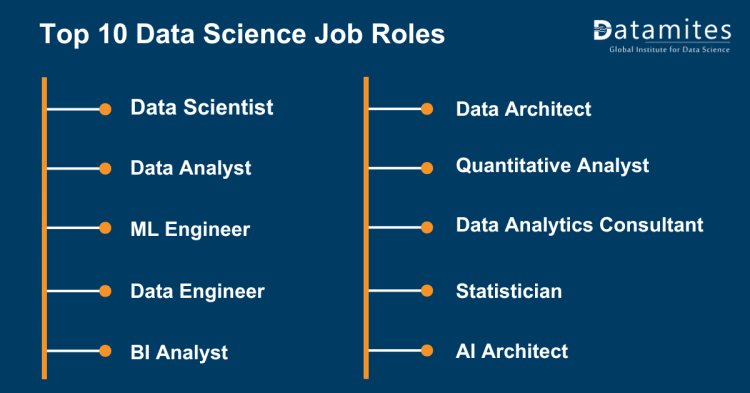
Top 10 Data Science Job Roles
The ongoing evolution and integration of data science are pivotal factors shaping the sustained growth and promising future prospects of the market and employment landscape in various data science job roles.
- Data Scientist: Analyzes complex data using statistical methods and machine learning to derive actionable insights for informed decision-making in diverse industries.
- Data Analyst: Interprets and transforms data, utilizing statistical analysis and visualization to provide valuable insights for strategic decision-making in business.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Designs algorithms enabling systems to learn and make predictions autonomously, contributing to the development of intelligent applications.
- Data Engineer: Constructs and maintains data systems, ensuring reliable data flow within organizational infrastructure for efficient data generation and storage.
- Business Intelligence Analyst: Gathers and analyzes business data, creating reports and dashboards to facilitate strategic decision-making through actionable insights.
- Data Architect: Designs and manages data system structures, ensuring data accuracy, security, and alignment with organizational data strategy.
- Quantitative Analyst: Applies mathematical and statistical techniques to financial and business data for developing models and strategies in investment and risk management.
- Data Analytics Consultant: Works with organizations to provide data-driven solutions, offering expertise in data analysis and strategic recommendations to enhance decision-making.
- Statistician: Uses statistical methods to analyze data, offering insights into trends, patterns, and relationships for decision-making across industries.
- AI Architect: Designs and oversees the implementation of AI solutions, developing architecture and infrastructure to support machine learning models aligned with organizational goals.
Types of Companies Hiring Data Scientists:
As data science continues to evolve, companies in diverse sectors increasingly seek professionals who can extract meaningful insights from complex data. The collaborative efforts between these industries and data scientists contribute not only to the growth of businesses but also to the overall advancement of technology and innovation.
According to recent findings from Forbes, around 5 percent of positions in data analytics and data science are located within the realms of IT, finance, insurance, and related professional services. The following sectors prominently feature among those actively recruiting data scientists:
- Tech Giants: Google, Amazon, and Facebook are leading employers.
- Financial Corporations: Firms like JPMorgan and Goldman Sachs.
- Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals: Leveraging data for patient care and drug development.
- Retail and E-commerce: Utilizing data for customer insights and market trends.
- Automotive and Manufacturing: Implementing AI and ML for innovation and efficiency.
Global Salary Trends in Data Science
The data science profession not only offers diverse career paths but also presents lucrative salary prospects across the globe. Data science salaries worldwide vary significantly by region, reflecting the local demand for data science skills and the cost of living.
- United Kingdom: Average salary of £50,567 per year (Indeed).
- Canada: Annual average salary of CAD 90,563 (Indeed).
- United States: High earning potential with an average of $124,867 per year (Indeed).
- South Africa: Average earnings are ZAR 451,297 annually (Payscale).
- India: Approximately INR ₹12,00,000 per annum (Glassdoor).
- Australia: Average salary is AUD 115,750 annually (Indeed).
- Switzerland: Average annual salary of CHF 117,024 (Glassdoor).
- United Arab Emirates: Average salary of AED 187,561 per annum (Indeed).
- Saudi Arabia: Average annual earnings of SAR 154,839 (Payscale).
- Germany: Around €56,036 per year on average (Payscale).
These figures highlight the global recognition and value of data science expertise. Data scientists not only enjoy a competitive salary but also have the potential to significantly impact business strategies and innovations. This global demand for data science skills underscores the career's resilience and growth potential in an increasingly data-driven world.

Educational Pathways and Prerequisites for Data Science
The journey into data science typically begins with a strong foundational education. Most data science roles require at least a bachelor's degree, often in fields like computer science, statistics, mathematics, or a related area. However, the complexity and depth of data science often necessitate further educational qualifications.
Need for Advanced Degrees:
- Many data scientists hold advanced degrees such as Master's or Ph.D.s in their field.
- These programs offer deeper insights into key areas like machine learning, big data analytics, and advanced statistical methods.
- Advanced degrees also provide opportunities for research and specialization in niche areas of data science.
Online Learning Resources and Courses:
- With the rise of digital education platforms, numerous online courses and certifications have become accessible.
- DataMites offers a variety of data science courses and certification programs, tailored to meet the evolving demands of the industry.
- These programs are structured to provide both theoretical understanding and practical application, covering areas like machine learning, AI, and big data analytics.
Significance of Hands-On Training:
- Practical experience is crucial in data science. Many courses include real-world projects, internships, or capstones to provide hands-on experience.
- Engaging in Kaggle competitions, contributing to open-source projects, or working on personal data projects can also enhance practical skills.
- Employers often look for candidates with a portfolio that demonstrates their ability to apply data science principles effectively.
The educational path for a career in data science is diverse and flexible, catering to various learning styles and career goals. Whether through formal university education, online courses, or self-directed learning projects, acquiring the right mix of theoretical knowledge and practical experience is key to success in this field.
Read these below articles:
- Data Science Career Scope in India
- Data Science Career Scope in Bangalore
- Data Science Career Scope in Chennai
Skills and Tools for Aspiring Data Scientists
Aspiring data scientists need to equip themselves with a blend of technical skills and tools to excel in this dynamic field. Here's an outline of essential skills and tools necessary for data scientists:
Programming Skills:
- R and SAS: Used for statistical analysis and data visualization. R is particularly favored in academia and research, while SAS is widely used in business analytics.
- Python: A versatile language essential for data science, known for its simplicity and wide range of libraries like Pandas, NumPy, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch.
- Test-Driven Development in Python: Developing code in Python with a focus on testing first ensures that the code is reliable and reduces the number of bugs.
Familiarity with Data Science Tools:
- Tableau: An impactful instrument for crafting engaging data visualizations with interactivity.
- Hadoop: Essential for processing large datasets using distributed computing.
- Apache Spark: Known for its speed in handling big data analytics, Spark is an improvement over Hadoop and can perform complex data processing tasks.
Database and SQL Knowledge:
- Proficiency in SQL (Structured Query Language) is crucial for data manipulation and retrieval from relational databases.
- Understanding of NoSQL databases like MongoDB or Cassandra can be beneficial.
Collaborative Skills:
- Familiarity with platforms like GitHub is important for version control, collaboration, and showcasing projects.
- Ability to work in teams and communicate effectively with both technical and non-technical stakeholders is crucial.
Other Important Skills:
- Basic understanding of machine learning algorithms and principles.
- Strong analytical skills to interpret complex data.
- Proficiency in data cleaning and preprocessing.
For data scientists, continuous learning and staying updated with the latest technologies and methodologies in the field are key. Engaging in real-world projects, participating in online forums, and contributing to open-source projects can further enhance these skills and tool proficiencies.
Steps to Launching a Data Science Career
Launching a data scientist career involves several strategic steps, from gaining the necessary education and skills to landing your first job in the field. Here is a guide to assist you in commencing your journey:
Acquire Relevant Education and Certifications:
- Begin with a strong foundation in a relevant field like computer science, mathematics, or statistics.
- Pursue certifications in data science to gain specialized knowledge. Certifications from reputed institutions or platforms can add significant value to your resume.
- Focus on learning key programming languages (Python, R) and tools (SQL, Tableau) essential for data science roles.
Undertake Internships:
- Internships provide invaluable real-world experience, offering a glimpse into the daily work of a data scientist.
- Seek internships in companies or research institutions where you can work on actual data science projects.
- Use data science internships to build a network of professional contacts and to understand different industry demands and work cultures.
Entry-Level Job Opportunities:
- Begin with roles like Data Analyst, Junior Data Scientist, or Business Intelligence Analyst. These positions often serve as stepping stones to more advanced data science roles.
- In entry-level roles, focus on honing your skills in data cleaning, analysis, visualization, and basic model building.
Progressing to Advanced Roles:
- As you gain experience, start taking on more complex projects that involve machine learning, predictive modeling, or deep learning.
- Continuously learn and update your skills. The field of data science is always evolving, so staying current with the latest technologies and methodologies is crucial.
- Seek roles that offer you more responsibility, such as leading a team, managing large-scale projects, or even transitioning into specialized roles like Machine Learning Engineer or Data Architect.
Continuous Learning and Networking:
- Attend workshops, webinars, and conferences to stay updated with the latest trends in data science.
- Engage with the data science community through forums, LinkedIn groups, or local meetups. Networking can open up new job opportunities and collaborations.
Build a Strong Portfolio:
- Document your projects, contributions to open-source, and any relevant work experience in a portfolio. This can be a powerful tool when applying for jobs or higher positions.
Remember, a career in data science is not just about technical skills but also about continuous learning, adaptability, and a keen sense to solve real-world problems with data.
Real-World Applications of Data Science
Data science finds its application in a myriad of real-world business scenarios. One of the most notable examples is Netflix, a global leader in streaming entertainment. Here's how data science plays a crucial role in companies like Netflix:
User Engagement Analysis:
- Netflix uses data science to monitor and analyze user interactions with its platform.
- By tracking user activities such as what they watch, when they pause or stop, and their browsing patterns, Netflix gains insights into viewer preferences and behaviors.
- This data helps Netflix understand what keeps viewers engaged, leading to strategies that enhance user experience and retention.
Recommendation Systems:
- One of the most significant applications of data science at Netflix is its recommendation system.
- The system analyzes vast amounts of data to suggest shows and movies to users based on their viewing history, ratings, and preferences.
- This personalized recommendation engine is key to Netflix's ability to keep users engaged and subscribed, as it helps users discover content that aligns with their tastes.
Content Development:
- Netflix also leverages data science in deciding which content to produce or acquire.
- By analyzing data on popular genres, viewer demographics, and successful content, Netflix can make informed decisions on what kind of shows or movies to invest in.
- This data-driven approach to content creation has led to the production of highly successful series and films that cater to a diverse global audience.
Also refer these below articles:
- What would be the Data Science Course Fee in India?
- Data Science Course Fee in Chennai
- Data Science Course Fee in Bangalore
In addition to Netflix, many other companies across various industries use data science for similar purposes, such as enhancing customer experience, developing targeted marketing strategies, optimizing supply chains, and much more. This widespread application of data science underscores its value in driving business success and innovation in the modern data-driven world.
Embarking on a data science career is a journey through a dynamic and evolving field. Key steps include gaining foundational knowledge in computer science or statistics, enhancing skills in programming languages like Python and R, and mastering tools such as Tableau and Hadoop. Practical experience through internships is crucial, offering insights into real-world applications. Career paths vary from data analysis to engineering, each with competitive salaries reflecting the growing industry demand. Staying updated with trends and continuous learning are vital. As you step into this field, you join the forefront of technological innovation, shaping the future with data-driven insights.
DataMites Institute is a global leader in data science and artificial intelligence education, offering the Certified Data Scientist Course. Recognized for its commitment to excellence, the program equips students with cutting-edge skills in data analysis, machine learning, and AI. The course culminates in an IABAC certification, validating the expertise of graduates and positioning them for success in the dynamic field of data science.





