Instructor Led Live Online
Self Learning + Live Mentoring
Customize Your Training


MODULE 1 : ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE OVERVIEW
• Evolution Of Human Intelligence
• What Is Artificial Intelligence?
• History Of Artificial Intelligence
• Why Artificial Intelligence Now?
• Areas Of Artificial Intelligence
• AI Vs Data Science Vs Machine Learning
MODULE 2 : DEEP LEARNING INTRODUCTION
• Deep Neural Network
• Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
• Feature Learning in Deep Networks
• Applications of Deep Learning Networks
MODULE3 : TENSORFLOW FOUNDATION
• TensorFlow Structure and Modules
• Hands-On:ML modeling with TensorFlow
MODULE 4 : COMPUTER VISION INTRODUCTION
• Image Basics
• Convolution Neural Network (CNN)
• Image Classification with CNN
• Hands-On: Cat vs Dogs Classification with CNN Network
MODULE 5 : NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING (NLP)
• NLP Introduction
• Bag of Words Models
• Word Embedding
• Hands-On:BERT Algorithm
MODULE 6 : AI ETHICAL ISSUES AND CONCERNS
• Issues And Concerns Around Ai
• Ai And Ethical Concerns
• Ai And Bias
• Ai:Ethics, Bias, And Trust
MODULE 1 : PYTHON BASICS
• Introduction of python
• Installation of Python and IDE
• Python Variables
• Python basic data types
• Number & Booleans, strings
• Arithmetic Operators
• Comparison Operators
• Assignment Operators
MODULE 2 : PYTHON CONTROL STATEMENTS
• IF Conditional statement
• IF-ELSE
• NESTED IF
• Python Loops basics
• WHILE Statement
• FOR statements
• BREAK and CONTINUE statements
MODULE 3 : PYTHON DATA STRUCTURES
• Basic data structure in python
• Basics of List
• List: Object, methods
• Tuple: Object, methods
• Sets: Object, methods
• Dictionary: Object, methods
MODULE 4 : PYTHON FUNCTIONS
• Functions basics
• Function Parameter passing
• Lambda functions
• Map, reduce, filter functions
MODULE 1 : OVERVIEW OF STATISTICS
• Introduction to Statistics
• Descriptive And Inferential Statistics
• Basic Terms Of Statistics
• Types Of Data
MODULE 2 : HARNESSING DATA
• Random Sampling
• Sampling With Replacement And Without Replacement
• Cochran's Minimum Sample Size
• Types of Sampling
• Simple Random Sampling
• Stratified Random Sampling
• Cluster Random Sampling
• Systematic Random Sampling
• Multi stage Sampling
• Sampling Error
• Methods Of Collecting Data
MODULE 3 : EXPLORATORY DATA ANALYSIS
• Exploratory Data Analysis Introduction
• Measures Of Central Tendencies: Mean,Median And Mode
• Measures Of Central Tendencies: Range, Variance And Standard Deviation
• Data Distribution Plot: Histogram
• Normal Distribution & Properties
• Z Value / Standard Value
• Empherical Rule and Outliers
• Central Limit Theorem
• Normality Testing
• Skewness & Kurtosis
• Measures Of Distance: Euclidean, Manhattan And Minkowski Distance
• Covariance & Correlation
MODULE 4 : HYPOTHESIS TESTING
• Hypothesis Testing Introduction
• P- Value, Critical Region
• Types of Hypothesis Testing
• Hypothesis Testing Errors : Type I And Type II
• Two Sample Independent T-test
• Two Sample Relation T-test
• One Way Anova Test
• Application of Hypothesis testing
MODULE 1: MACHINE LEARNING INTRODUCTION
• What Is ML? ML Vs AI
• Clustering, Classification And Regression
• Supervised Vs Unsupervised
MODULE 2: PYTHON NUMPY PACKAGE
• Introduction to Numpy Package
• Array as Data Structure
• Core Numpy functions
• Matrix Operations, Broadcasting in Arrays
MODULE 3: PYTHON PANDAS PACKAGE
• Introduction to Pandas package
• Series in Pandas
• Data Frame in Pandas
• File Reading in Pandas
• Data munging with Pandas
MODULE 4: VISUALIZATION WITH PYTHON - Matplotlib
• Visualization Packages (Matplotlib)
• Components Of A Plot, Sub-Plots
• Basic Plots: Line, Bar, Pie, Scatter
MODULE 5: PYTHON VISUALIZATION PACKAGE - SEABORN
• Seaborn: Basic Plot
• Advanced Python Data Visualizations
MODULE 6: ML ALGO: LINEAR REGRESSION
• Introduction to Linear Regression
• How it works: Regression and Best Fit Line
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 7: ML ALGO: LOGISTIC REGRESSION
• Introduction to Logistic Regression
• How it works: Classification & Sigmoid Curve
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 8: ML ALGO: K MEANS CLUSTERING
• Understanding Clustering (Unsupervised)
• K Means Algorithm
• How it works : K Means theory
• Modeling in Python
MODULE 9: ML ALGO: KNN
• Introduction to KNN
• How It Works: Nearest Neighbor Concept
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 1: FEATURE ENGINEERING
• Introduction to Feature Engineering
• Feature Engineering Techniques: Encoding, Scaling, Data Transformation
• Handling Missing values, handling outliers
• Creation of Pipeline
• Use case for feature engineering
MODULE 2: ML ALGO: SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE (SVM)
• Introduction to SVM
• How It Works: SVM Concept, Kernel Trick
• Modeling and Evaluation of SVM in Python
MODULE 3: PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS (PCA)
• Building Blocks Of PCA
• How it works: Finding Principal Components
• Modeling PCA in Python
MODULE 4: ML ALGO: DECISION TREE
• Introduction to Decision Tree & Random Forest
• How it works
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 5: ENSEMBLE TECHNIQUES - BAGGING
• Introduction to Ensemble technique
• Bagging and How it works
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 6: ML ALGO: NAÏVE BAYES
• Introduction to Naive Bayes
• How it works: Bayes' Theorem
• Naive Bayes For Text Classification
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 7: GRADIENT BOOSTING, XGBOOST
• Introduction to Boosting and XGBoost
• How it works?
• Modeling and Evaluation of in Python
MODULE 1: TIME SERIES FORECASTING - ARIMA
• What is Time Series?
• Trend, Seasonality, cyclical and random
• Stationarity of Time Series
• Autoregressive Model (AR)
• Moving Average Model (MA)
• ARIMA Model
• Autocorrelation and AIC
• Time Series Analysis in Python
MODULE 2: SENTIMENT ANALYSIS
• Introduction to Sentiment Analysis
• NLTK Package
• Case study: Sentiment Analysis on Movie Reviews
MODULE 3: REGULAR EXPRESSIONS WITH PYTHON
• Regex Introduction
• Regex codes
• Text extraction with Python Regex
MODULE 4: ML MODEL DEPLOYMENT WITH FLASK
• Introduction to Flask
• URL and App routing
• Flask application – ML Model deployment
MODULE 5: ADVANCED DATA ANALYSIS WITH MS EXCEL
• MS Excel core Functions
• Advanced Functions (VLOOKUP, INDIRECT..)
• Linear Regression with EXCEL
• Data Table
• Goal Seek Analysis
• Pivot Table
• Solving Data Equation with EXCEL
MODULE 6: AWS CLOUD FOR DATA SCIENCE
• Introduction of cloud
• Difference between GCC, Azure,AWS
• AWS Service ( EC2 instance)
MODULE 7: AZURE FOR DATA SCIENCE
• Introduction to AZURE ML studio
• Data Pipeline
• ML modeling with Azure
MODULE 8: INTRODUCTION TO DEEP LEARNING
• Introduction to Artificial Neural Network, Architecture
• Artificial Neural Network in Python
• Introduction to Convolutional Neural Network, Architecture
• Convolutional Neural Network in Python
MODULE 1: DATABASE INTRODUCTION
• DATABASE Overview
• Key concepts of database management
• Relational Database Management System
• CRUD operations
MODULE 2: SQL BASICS
• Introduction to Databases
• Introduction to SQL
• SQL Commands
• MY SQL workbench installation
MODULE 3: DATA TYPES AND CONSTRAINTS
• Numeric, Character, date time data type
• Primary key, Foreign key, Not null
• Unique, Check, default, Auto increment
MODULE 4: DATABASES AND TABLES (MySQL)
• Create database
• Delete database
• Show and use databases
• Create table, Rename table
• Delete table, Delete table records
• Create new table from existing data types
• Insert into, Update records
• Alter table
MODULE 5: SQL JOINS
• Inner join
• Outer join
• Left join
• Right join
• Cross join
• Self join
• Windows functions: Over, Partition , Rank
MODULE 6: SQL COMMANDS AND CLAUSES
• Select, Select distinct
• Aliases, Where clause
• Relational operators, Logical
• Between, Order by, In
• Like, Limit, null/not null, group by
• Having, Sub queries
MODULE 7: DOCUMENT DB/NO-SQL DB
• Introduction of Document DB
• Document DB vs SQL DB
• Popular Document DBs
• MongoDB basics
• Data format and Key methods
MODULE 1: GIT INTRODUCTION
• Purpose of Version Control
• Popular Version control tools
• Git Distribution Version Control
• Terminologies
• Git Workflow
• Git Architecture
MODULE 2: GIT REPOSITORY and GitHub
• Git Repo Introduction
• Create New Repo with Init command
• Git Essentials: Copy & User Setup
• Mastering Git and GitHub
MODULE 3: COMMITS, PULL, FETCH AND PUSH
• Code commits
• Pull, Fetch and conflicts resolution
• Pushing to Remote Repo
MODULE 4: TAGGING, BRANCHING AND MERGING
• Organize code with branches
• Checkout branch
• Merge branches
• Editing Commits
• Commit command Amend flag
• Git reset and revert
MODULE 5: GIT WITH GITHUB AND BITBUCKET
• Creating GitHub Account
• Local and Remote Repo
• Collaborating with other developers
MODULE 1: BIG DATA INTRODUCTION
MODULE 2: HDFS AND MAP REDUCE
MODULE 3: PYSPARK FOUNDATION
MODULE 4: SPARK SQL and HADOOP HIVE
MODULE 1: TABLEAU FUNDAMENTALS
• Introduction to Business Intelligence & Introduction to Tableau
• Interface Tour, Data visualization: Pie chart, Column chart, Bar chart.
• Bar chart, Tree Map, Line Chart
• Area chart, Combination Charts, Map
• Dashboards creation, Quick Filters
• Create Table Calculations
• Create Calculated Fields
• Create Custom Hierarchies
MODULE 2: POWER-BI BASICS
• Power BI Introduction
• Basics Visualizations
• Dashboard Creation
• Basic Data Cleaning
• Basic DAX FUNCTION
MODULE 3 : DATA TRANSFORMATION TECHNIQUES
• Exploring Query Editor
• Data Cleansing and Manipulation:
• Creating Our Initial Project File
• Connecting to Our Data Source
• Editing Rows
• Changing Data Types
• Replacing Values
MODULE 4 : CONNECTING TO VARIOUS DATA SOURCES
• Connecting to a CSV File
• Connecting to a Webpage
• Extracting Characters
• Splitting and Merging Columns
• Creating Conditional Columns
• Creating Columns from Examples
• Create Data Model
MODULE 1: NEURAL NETWORKS
• Structure of neural networks
• Neural network - core concepts(Weight initialization)
• Neural network - core concepts(Optimizer)
• Neural network - core concepts(Need of activation)
• Neural network - core concepts(MSE & RMSE)
• Feed forward algorithm
• Backpropagation
MODULE 2: IMPLEMENTING DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS
• Introduction to neural networks with tf2.X
• Simple deep learning model in Keras (tf2.X)
• Building neural network model in TF2.0 for MNIST dataset
MODULE 3: DEEP COMPUTER VISION - IMAGE RECOGNITION
• Convolutional neural networks (CNNs)
• CNNs with Keras-part1
• CNNs with Keras-part2
• Transfer learning in CNN
• Flowers dataset with tf2.X(part-1)
• Flowers dataset with tf2.X(part-2)
• Examining x-ray with CNN model
MODULE 4 : DEEP COMPUTER VISION - OBJECT DETECTION
• What is Object detection
• Methods of Object Detections
• Metrics of Object detection
• Bounding Box regression
• labelimg
• RCNN
• Fast RCNN
• Faster RCNN
• SSD
• YOLO Implementation
• Object detection using cv2
MODULE 5: RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORK
• RNN introduction
• Sequences with RNNs
• Long short-term memory networks(part 1)
• Long short-term memory networks(part 2)
• Bi-directional RNN and LSTM
• Examples of RNN applications
MODULE 6: NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING (NLP)
• Introduction to Natural language processing
• Working with Text file
• Working with pdf file
• Introduction to regex
• Regex part 1
• Regex part 2
• Word Embedding
• RNN model creation
• Transformers and BERT
• Introduction to GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer)
• State of art NLP and projects
MODULE 7: PROMPT ENGINEERING
• Introduction to Prompt Engineering
• Understanding the Role of Prompts in AI Systems
• Design Principles for Effective Prompts
• Techniques for Generating and Optimizing Prompts
• Applications of Prompt Engineering in Natural Language Processing
MODULE 8: REINFORCEMENT LEARNING
• Markov decision process
• Fundamental equations in RL
• Model-based method
• Dynamic programming model free methods
MODULE 9: DEEP REINFORCEMENT LEARNING
• Architectures of deep Q learning
• Deep Q learning
• Reinforcement Learning Projects with OpenAI Gym
MODULE 10: Gen AI
• Gan introduction, Core Concepts, and Applications
• Core concepts of GAN
• GAN applications
• Building GAN model with TensorFlow 2.X
• Introduction to GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer)
• Building a Question answer bot with the models on Hugging Face
MODULE 11: Gen AI
• Introduction to Autoencoder
• Basic Structure and Components of Autoencoders
• Types of Autoencoders: Vanilla, Denoising, Variational, Sparse, and Convolutional Autoencoders
• Training Autoencoders: Loss Functions, Optimization Techniques
• Applications of Autoencoders: Dimensionality Reduction, Anomaly Detection, Image
Artificial Intelligence (AI) embodies the replication of human cognitive processes through mechanized systems, predominantly within computer frameworks.
Machine Learning functions as a subset within AI, whereby machines are trained to discern patterns from data, facilitating autonomous predictions or decisions without explicit programming.
Integrating AI within business ventures encompasses various applications such as task automation, interactive chatbots for customer service, predictive data analysis, and customized marketing strategies, all aimed at amplifying operational efficacy and decision-making processes.
AI represents a broader conceptual framework endeavouring to emulate human intelligence, whereas Machine Learning constitutes a specific methodology within AI, concentrating on algorithmic learning from data.
Prominent programming languages in AI include Python, R, Java, and C++. Python, in particular, stands out due to its user-friendly nature and extensive libraries conducive to AI advancement.
While AI may streamline certain tasks, its primary function revolves around enhancing human capabilities rather than outright job displacement, heralding a shift in occupational roles and requisite skill sets.
Ethical quandaries in AI progression span concerns such as algorithmic bias, privacy infringements, and potential societal ramifications such as employment displacement and exacerbation of inequalities.
AI risks entail potential misapplications like deepfake technology, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and inadvertent repercussions stemming from biased or inadequately formulated algorithms.
The principal responsibilities of an AI engineer encompass crafting AI models, ensuring data integrity, refining algorithms, and fostering collaboration with interdisciplinary teams.
Top-earning roles in AI encompass machine learning engineer, data scientist, AI researcher, and AI architect, with salary discrepancies contingent on experience and geographical location.
Companies seeking AI talent include industry titans like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon, alongside startups, research entities, and enterprises spanning diverse sectors with vested interests in AI integration.
Proficiency in AI within the Malé can be attained through avenues such as online courses, academic programs at universities, or specialized training offered by tech entities and educational institutions.
Qualifications for AI roles in the Malé typically entail a degree in computer science, mathematics, or cognate disciplines, coupled with adeptness in programming and hands-on involvement in AI initiatives.
While certifications can bolster credibility and validate skills, hands-on experience and demonstrable project portfolios often carry greater weight in securing AI positions in the Malé.
The job landscape for AI professionals in the Malé is burgeoning, with escalating demand spanning sectors such as finance, healthcare, and burgeoning technology startups.
Transitioning to AI from a dissimilar career trajectory is feasible with the dedicated acquisition of pertinent skills and the cultivation of a robust portfolio showcasing AI proficiency.
Entry-level opportunities in AI for novices may encompass roles like an AI research assistant, data analyst, or junior machine learning engineer, prioritizing learning and skill cultivation.
AI's application in healthcare spans domains such as medical imaging analysis, drug discovery, formulation of personalized treatment regimens, and streamlining administrative tasks, all geared towards enhancing diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes.
To embark on an AI engineering trajectory in the Malé, focus on accruing pertinent skills through education, practical projects, and immersion in the AI community.
High-demand skills for AI vocations in the Malé encompass mastery of Python, comprehension of machine learning algorithms, adept data analysis capabilities, and adeptness in problem-solving.
DataMites presents a diverse portfolio of AI certifications in the Malé, including Artificial Intelligence Engineering, AI Expertise, Certified NLP Expertise, AI Management, and AI Foundations. These certifications provide extensive training across various AI technologies and their practical applications.
Eligibility for DataMites' AI training in the Malé extends to individuals with backgrounds in computer science, engineering, mathematics, or statistics. However, the program also welcomes participants from non-technical fields, fostering inclusivity and diverse participation.
The duration of DataMites' AI courses in Malé varies depending on the selected program, spanning from one to nine months. Flexible scheduling options, including weekdays and weekends, accommodate participants' availability.
To attain proficiency in AI within the Malé, consider enrolling in DataMites, a renowned institute specializing in data science and AI. DataMites offers tailored learning paths to individuals aspiring for excellence in AI.
DataMites' AI Expert training in the Malé provides participants with a robust foundation in AI fundamentals, machine learning, and practical implementations. Led by industry experts, the curriculum emphasizes hands-on learning, preparing individuals for real-world AI challenges.
DataMites in the Malé offers diverse payment options for AI course training, including cash, debit/credit cards, checks, EMI, PayPal, and net banking, ensuring convenience for participants.
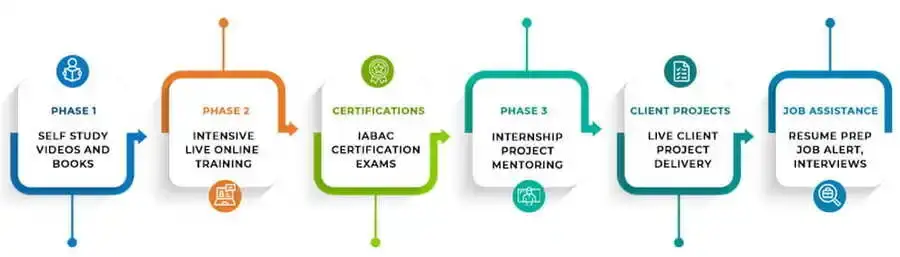
Yes, DataMites integrates live projects, including 10 Capstone projects and 1 Client Project, into its AI course in the Malé. These projects provide hands-on experience and practical learning opportunities for participants.
Indeed, participants in the Malé can attend help sessions aimed at enhancing their comprehension of AI topics, offering additional support and clarification as needed.
DataMites in the Malé adopts a case study-centric approach to AI training, delivering a meticulously crafted curriculum designed to meet industry demands and provide career-oriented education.
Choose DataMites' online AI training in the Malé for expert-led instruction, flexible learning options, and hands-on experience. Obtain industry-recognized certification while mastering machine learning and deep learning concepts, supported by career guidance and a vibrant learning community.
The fees for AI Training in the Malé offered by DataMites range from MVR 10,731 to MVR 28,543. with actual costs varying based on course selection and duration.
AI training sessions at DataMites in the Malé are led by Ashok Veda, a respected Data Science coach and AI Expert, along with mentors possessing real-world experience from prestigious institutions and companies.
Flexi-Pass offers flexible learning options for AI training in the Malé, allowing participants to customize their schedules and access a wealth of resources and mentorship tailored to their learning pace and commitments.
Upon completion of AI training in the Malé, participants receive IABAC Certification, globally recognized within the EU framework, validating their AI skills and knowledge.
Participants attending AI training sessions in the Malé need to present a valid photo ID, such as a national ID card or driver's license, to obtain participation certificates and schedule certification exams.
In the event of absences during AI training in the Malé, participants can access recorded sessions or seek mentor guidance for catch-up, ensuring continuous progress despite occasional absences.
Certainly, participants in the Malé can attend demo classes for AI courses before payment to evaluate the program's suitability firsthand.
Yes, DataMites in the Malé provides AI Courses paired with internships in select industries, offering practical experience to enhance participants' career prospects in AI roles.
DataMites' Placement Assistance Team organizes career mentoring sessions in the Malé, providing insights into various career paths in Data Science and AI, along with strategies for overcoming challenges.
The AI Foundation Course encompasses fundamental AI concepts, applications, and real-world examples, catering to individuals with varying technical backgrounds and interests in machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks.
The DataMites Placement Assistance Team(PAT) facilitates the aspirants in taking all the necessary steps in starting their career in Data Science. Some of the services provided by PAT are: -
The DataMites Placement Assistance Team(PAT) conducts sessions on career mentoring for the aspirants with a view of helping them realize the purpose they have to serve when they step into the corporate world. The students are guided by industry experts about the various possibilities in the Data Science career, this will help the aspirants to draw a clear picture of the career options available. Also, they will be made knowledgeable about the various obstacles they are likely to face as a fresher in the field, and how they can tackle.
No, PAT does not promise a job, but it helps the aspirants to build the required potential needed in landing a career. The aspirants can capitalize on the acquired skills, in the long run, to a successful career in Data Science.