Instructor Led Live Online
Self Learning + Live Mentoring
Customize Your Training


MODULE 1 : ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE OVERVIEW
• Evolution Of Human Intelligence
• What Is Artificial Intelligence?
• History Of Artificial Intelligence
• Why Artificial Intelligence Now?
• Areas Of Artificial Intelligence
• AI Vs Data Science Vs Machine Learning
MODULE 2 : DEEP LEARNING INTRODUCTION
• Deep Neural Network
• Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
• Feature Learning in Deep Networks
• Applications of Deep Learning Networks
MODULE3 : TENSORFLOW FOUNDATION
• TensorFlow Structure and Modules
• Hands-On:ML modeling with TensorFlow
MODULE 4 : COMPUTER VISION INTRODUCTION
• Image Basics
• Convolution Neural Network (CNN)
• Image Classification with CNN
• Hands-On: Cat vs Dogs Classification with CNN Network
MODULE 5 : NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING (NLP)
• NLP Introduction
• Bag of Words Models
• Word Embedding
• Hands-On:BERT Algorithm
MODULE 6 : AI ETHICAL ISSUES AND CONCERNS
• Issues And Concerns Around Ai
• Ai And Ethical Concerns
• Ai And Bias
• Ai:Ethics, Bias, And Trust
MODULE 1 : PYTHON BASICS
• Introduction of python
• Installation of Python and IDE
• Python Variables
• Python basic data types
• Number & Booleans, strings
• Arithmetic Operators
• Comparison Operators
• Assignment Operators
MODULE 2 : PYTHON CONTROL STATEMENTS
• IF Conditional statement
• IF-ELSE
• NESTED IF
• Python Loops basics
• WHILE Statement
• FOR statements
• BREAK and CONTINUE statements
MODULE 3 : PYTHON DATA STRUCTURES
• Basic data structure in python
• Basics of List
• List: Object, methods
• Tuple: Object, methods
• Sets: Object, methods
• Dictionary: Object, methods
MODULE 4 : PYTHON FUNCTIONS
• Functions basics
• Function Parameter passing
• Lambda functions
• Map, reduce, filter functions
MODULE 1 : OVERVIEW OF STATISTICS
• Introduction to Statistics
• Descriptive And Inferential Statistics
• Basic Terms Of Statistics
• Types Of Data
MODULE 2 : HARNESSING DATA
• Random Sampling
• Sampling With Replacement And Without Replacement
• Cochran's Minimum Sample Size
• Types of Sampling
• Simple Random Sampling
• Stratified Random Sampling
• Cluster Random Sampling
• Systematic Random Sampling
• Multi stage Sampling
• Sampling Error
• Methods Of Collecting Data
MODULE 3 : EXPLORATORY DATA ANALYSIS
• Exploratory Data Analysis Introduction
• Measures Of Central Tendencies: Mean,Median And Mode
• Measures Of Central Tendencies: Range, Variance And Standard Deviation
• Data Distribution Plot: Histogram
• Normal Distribution & Properties
• Z Value / Standard Value
• Empherical Rule and Outliers
• Central Limit Theorem
• Normality Testing
• Skewness & Kurtosis
• Measures Of Distance: Euclidean, Manhattan And Minkowski Distance
• Covariance & Correlation
MODULE 4 : HYPOTHESIS TESTING
• Hypothesis Testing Introduction
• P- Value, Critical Region
• Types of Hypothesis Testing
• Hypothesis Testing Errors : Type I And Type II
• Two Sample Independent T-test
• Two Sample Relation T-test
• One Way Anova Test
• Application of Hypothesis testing
MODULE 1: MACHINE LEARNING INTRODUCTION
• What Is ML? ML Vs AI
• Clustering, Classification And Regression
• Supervised Vs Unsupervised
MODULE 2: PYTHON NUMPY PACKAGE
• Introduction to Numpy Package
• Array as Data Structure
• Core Numpy functions
• Matrix Operations, Broadcasting in Arrays
MODULE 3: PYTHON PANDAS PACKAGE
• Introduction to Pandas package
• Series in Pandas
• Data Frame in Pandas
• File Reading in Pandas
• Data munging with Pandas
MODULE 4: VISUALIZATION WITH PYTHON - Matplotlib
• Visualization Packages (Matplotlib)
• Components Of A Plot, Sub-Plots
• Basic Plots: Line, Bar, Pie, Scatter
MODULE 5: PYTHON VISUALIZATION PACKAGE - SEABORN
• Seaborn: Basic Plot
• Advanced Python Data Visualizations
MODULE 6: ML ALGO: LINEAR REGRESSION
• Introduction to Linear Regression
• How it works: Regression and Best Fit Line
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 7: ML ALGO: LOGISTIC REGRESSION
• Introduction to Logistic Regression
• How it works: Classification & Sigmoid Curve
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 8: ML ALGO: K MEANS CLUSTERING
• Understanding Clustering (Unsupervised)
• K Means Algorithm
• How it works : K Means theory
• Modeling in Python
MODULE 9: ML ALGO: KNN
• Introduction to KNN
• How It Works: Nearest Neighbor Concept
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 1: FEATURE ENGINEERING
• Introduction to Feature Engineering
• Feature Engineering Techniques: Encoding, Scaling, Data Transformation
• Handling Missing values, handling outliers
• Creation of Pipeline
• Use case for feature engineering
MODULE 2: ML ALGO: SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE (SVM)
• Introduction to SVM
• How It Works: SVM Concept, Kernel Trick
• Modeling and Evaluation of SVM in Python
MODULE 3: PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS (PCA)
• Building Blocks Of PCA
• How it works: Finding Principal Components
• Modeling PCA in Python
MODULE 4: ML ALGO: DECISION TREE
• Introduction to Decision Tree & Random Forest
• How it works
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 5: ENSEMBLE TECHNIQUES - BAGGING
• Introduction to Ensemble technique
• Bagging and How it works
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 6: ML ALGO: NAÏVE BAYES
• Introduction to Naive Bayes
• How it works: Bayes' Theorem
• Naive Bayes For Text Classification
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 7: GRADIENT BOOSTING, XGBOOST
• Introduction to Boosting and XGBoost
• How it works?
• Modeling and Evaluation of in Python
MODULE 1: TIME SERIES FORECASTING - ARIMA
• What is Time Series?
• Trend, Seasonality, cyclical and random
• Stationarity of Time Series
• Autoregressive Model (AR)
• Moving Average Model (MA)
• ARIMA Model
• Autocorrelation and AIC
• Time Series Analysis in Python
MODULE 2: SENTIMENT ANALYSIS
• Introduction to Sentiment Analysis
• NLTK Package
• Case study: Sentiment Analysis on Movie Reviews
MODULE 3: REGULAR EXPRESSIONS WITH PYTHON
• Regex Introduction
• Regex codes
• Text extraction with Python Regex
MODULE 4: ML MODEL DEPLOYMENT WITH FLASK
• Introduction to Flask
• URL and App routing
• Flask application – ML Model deployment
MODULE 5: ADVANCED DATA ANALYSIS WITH MS EXCEL
• MS Excel core Functions
• Advanced Functions (VLOOKUP, INDIRECT..)
• Linear Regression with EXCEL
• Data Table
• Goal Seek Analysis
• Pivot Table
• Solving Data Equation with EXCEL
MODULE 6: AWS CLOUD FOR DATA SCIENCE
• Introduction of cloud
• Difference between GCC, Azure,AWS
• AWS Service ( EC2 instance)
MODULE 7: AZURE FOR DATA SCIENCE
• Introduction to AZURE ML studio
• Data Pipeline
• ML modeling with Azure
MODULE 8: INTRODUCTION TO DEEP LEARNING
• Introduction to Artificial Neural Network, Architecture
• Artificial Neural Network in Python
• Introduction to Convolutional Neural Network, Architecture
• Convolutional Neural Network in Python
MODULE 1: DATABASE INTRODUCTION
• DATABASE Overview
• Key concepts of database management
• Relational Database Management System
• CRUD operations
MODULE 2: SQL BASICS
• Introduction to Databases
• Introduction to SQL
• SQL Commands
• MY SQL workbench installation
MODULE 3: DATA TYPES AND CONSTRAINTS
• Numeric, Character, date time data type
• Primary key, Foreign key, Not null
• Unique, Check, default, Auto increment
MODULE 4: DATABASES AND TABLES (MySQL)
• Create database
• Delete database
• Show and use databases
• Create table, Rename table
• Delete table, Delete table records
• Create new table from existing data types
• Insert into, Update records
• Alter table
MODULE 5: SQL JOINS
• Inner join
• Outer join
• Left join
• Right join
• Cross join
• Self join
• Windows functions: Over, Partition , Rank
MODULE 6: SQL COMMANDS AND CLAUSES
• Select, Select distinct
• Aliases, Where clause
• Relational operators, Logical
• Between, Order by, In
• Like, Limit, null/not null, group by
• Having, Sub queries
MODULE 7: DOCUMENT DB/NO-SQL DB
• Introduction of Document DB
• Document DB vs SQL DB
• Popular Document DBs
• MongoDB basics
• Data format and Key methods
MODULE 1: GIT INTRODUCTION
• Purpose of Version Control
• Popular Version control tools
• Git Distribution Version Control
• Terminologies
• Git Workflow
• Git Architecture
MODULE 2: GIT REPOSITORY and GitHub
• Git Repo Introduction
• Create New Repo with Init command
• Git Essentials: Copy & User Setup
• Mastering Git and GitHub
MODULE 3: COMMITS, PULL, FETCH AND PUSH
• Code commits
• Pull, Fetch and conflicts resolution
• Pushing to Remote Repo
MODULE 4: TAGGING, BRANCHING AND MERGING
• Organize code with branches
• Checkout branch
• Merge branches
• Editing Commits
• Commit command Amend flag
• Git reset and revert
MODULE 5: GIT WITH GITHUB AND BITBUCKET
• Creating GitHub Account
• Local and Remote Repo
• Collaborating with other developers
MODULE 1: BIG DATA INTRODUCTION
MODULE 2: HDFS AND MAP REDUCE
MODULE 3: PYSPARK FOUNDATION
MODULE 4: SPARK SQL and HADOOP HIVE
MODULE 1: TABLEAU FUNDAMENTALS
• Introduction to Business Intelligence & Introduction to Tableau
• Interface Tour, Data visualization: Pie chart, Column chart, Bar chart.
• Bar chart, Tree Map, Line Chart
• Area chart, Combination Charts, Map
• Dashboards creation, Quick Filters
• Create Table Calculations
• Create Calculated Fields
• Create Custom Hierarchies
MODULE 2: POWER-BI BASICS
• Power BI Introduction
• Basics Visualizations
• Dashboard Creation
• Basic Data Cleaning
• Basic DAX FUNCTION
MODULE 3 : DATA TRANSFORMATION TECHNIQUES
• Exploring Query Editor
• Data Cleansing and Manipulation:
• Creating Our Initial Project File
• Connecting to Our Data Source
• Editing Rows
• Changing Data Types
• Replacing Values
MODULE 4 : CONNECTING TO VARIOUS DATA SOURCES
• Connecting to a CSV File
• Connecting to a Webpage
• Extracting Characters
• Splitting and Merging Columns
• Creating Conditional Columns
• Creating Columns from Examples
• Create Data Model
MODULE 1: NEURAL NETWORKS
• Structure of neural networks
• Neural network - core concepts(Weight initialization)
• Neural network - core concepts(Optimizer)
• Neural network - core concepts(Need of activation)
• Neural network - core concepts(MSE & RMSE)
• Feed forward algorithm
• Backpropagation
MODULE 2: IMPLEMENTING DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS
• Introduction to neural networks with tf2.X
• Simple deep learning model in Keras (tf2.X)
• Building neural network model in TF2.0 for MNIST dataset
MODULE 3: DEEP COMPUTER VISION - IMAGE RECOGNITION
• Convolutional neural networks (CNNs)
• CNNs with Keras-part1
• CNNs with Keras-part2
• Transfer learning in CNN
• Flowers dataset with tf2.X(part-1)
• Flowers dataset with tf2.X(part-2)
• Examining x-ray with CNN model
MODULE 4 : DEEP COMPUTER VISION - OBJECT DETECTION
• What is Object detection
• Methods of Object Detections
• Metrics of Object detection
• Bounding Box regression
• labelimg
• RCNN
• Fast RCNN
• Faster RCNN
• SSD
• YOLO Implementation
• Object detection using cv2
MODULE 5: RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORK
• RNN introduction
• Sequences with RNNs
• Long short-term memory networks(part 1)
• Long short-term memory networks(part 2)
• Bi-directional RNN and LSTM
• Examples of RNN applications
MODULE 6: NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING (NLP)
• Introduction to Natural language processing
• Working with Text file
• Working with pdf file
• Introduction to regex
• Regex part 1
• Regex part 2
• Word Embedding
• RNN model creation
• Transformers and BERT
• Introduction to GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer)
• State of art NLP and projects
MODULE 7: PROMPT ENGINEERING
• Introduction to Prompt Engineering
• Understanding the Role of Prompts in AI Systems
• Design Principles for Effective Prompts
• Techniques for Generating and Optimizing Prompts
• Applications of Prompt Engineering in Natural Language Processing
MODULE 8: REINFORCEMENT LEARNING
• Markov decision process
• Fundamental equations in RL
• Model-based method
• Dynamic programming model free methods
MODULE 9: DEEP REINFORCEMENT LEARNING
• Architectures of deep Q learning
• Deep Q learning
• Reinforcement Learning Projects with OpenAI Gym
MODULE 10: Gen AI
• Gan introduction, Core Concepts, and Applications
• Core concepts of GAN
• GAN applications
• Building GAN model with TensorFlow 2.X
• Introduction to GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer)
• Building a Question answer bot with the models on Hugging Face
MODULE 11: Gen AI
• Introduction to Autoencoder
• Basic Structure and Components of Autoencoders
• Types of Autoencoders: Vanilla, Denoising, Variational, Sparse, and Convolutional Autoencoders
• Training Autoencoders: Loss Functions, Optimization Techniques
• Applications of Autoencoders: Dimensionality Reduction, Anomaly Detection, Image
Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands as a domain within computer science, dedicated to crafting systems capable of executing tasks traditionally necessitating human intellect, including learning, problem-solving, reasoning, perception, and language comprehension.
Prerequisites for AI roles in Poland typically entail a degree in computer science, mathematics, engineering, or cognate disciplines. Proficiency in programming languages like Python, familiarity with machine learning algorithms, and adeptness with AI frameworks and tools constitute essential qualifications.
While Artificial Intelligence Certifications can bolster one's credibility and knowledge in Poland's AI sector, they aren't invariably obligatory. Practical experience, engagement in projects, and a robust grasp of AI principles often hold greater value.
AI permeates everyday life, from virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to recommendation systems on streaming platforms such as Netflix and Spotify. Other instances include personalized advertisements, smart home devices, virtual customer service agents, and predictive text input on smartphones.
In healthcare, AI finds application in tasks such as interpreting medical imaging, drug discovery, devising personalized treatment plans, predictive analytics for disease prevention, and handling administrative duties like patient scheduling. Its integration serves to enhance diagnostic accuracy, streamline operations, and propel medical research forward.
Artificial intelligence leaves its mark on the entertainment sector by facilitating personalized recommendations on streaming platforms, algorithm-driven content creation, augmenting visual effects in films, and optimizing marketing strategies. Additionally, it aids in audience analysis, trend prognostication, and revenue maximization for production entities.
To initiate an AI career sans prior experience, commence by acquainting yourself with AI fundamentals via online courses, tutorials, and literature. Establish a sturdy grounding in programming, statistics, and linear algebra. Gain hands-on experience by engaging in projects, competitions, or contributing to open-source AI initiatives. Networking and securing mentorship can also prove invaluable.
A background in computer science, mathematics, statistics, engineering, or related disciplines serves as the norm for AI careers. However, specialized AI-related degrees such as a Master's or Ph.D. in Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, or Data Science can furnish tailored expertise and competencies.
Some of the highest-paying positions in AI encompass AI research scientists, machine learning engineers, data scientists, AI consultants, and AI product managers. Remuneration varies based on factors such as experience, location, industry, and company size.
Esteemed tech conglomerates such as Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Facebook, and Apple perennially seek AI professionals. Moreover, entities across diverse sectors like healthcare, finance, automotive, and retail evince a demand for AI talent to harness AI-driven technologies.
Mastery of AI can be achieved through online artificial intelligence courses in Poland, workshops, university programs, or specialized training institutes. Practical involvement in projects and the pursuit of internships or mentorships offer crucial hands-on experience.
Artificial Intelligence Engineers in Poland can anticipate significant remuneration, with an average annual salary of PLN 185,981, as reported by the Economic Research Institute, reflecting the robust earning potential within the Polish AI engineering sector.
AI finds utility in education through avenues such as personalized learning experiences, adaptive tutoring systems, automated grading, analysis of student engagement, and facilitation of administrative tasks like scheduling and resource allocation. Its incorporation serves to heighten teaching efficacy, elevate student outcomes, and enhance overall educational efficiency.
In Poland, sought-after skills for AI careers encompass proficiency in programming languages like Python, mastery of machine learning algorithms, adeptness in data manipulation and analysis, and familiarity with AI frameworks such as TensorFlow and PyTorch. Soft skills like problem-solving, critical thinking, and effective communication are also highly prized.
To embark on a career as an AI engineer in Poland, cultivate a robust foundation in programming, mathematics, and machine learning. Gain practical experience by immersing yourself in projects and participating in competitions. Pursue pertinent education or certifications, network with industry professionals, and stay abreast of the latest AI developments.
Core responsibilities of an AI engineer encompass conceptualizing and crafting AI models and algorithms, data collection and preprocessing, model training and evaluation, deployment of AI solutions, and ongoing optimization efforts. Collaboration with cross-functional teams to grasp business requirements and seamlessly integrate AI into products or systems also falls within their purview.
In e-commerce, artificial intelligence assumes a multifaceted role, manifesting in functions such as personalized product recommendations, dynamic pricing optimization, fraud detection, customer segmentation, chatbots for customer service, and supply chain optimization. Its integration serves to enrich user experiences, amplify sales, and optimize operational efficiency for e-commerce enterprises.
Yes, transitioning to AI from a disparate career path is indeed viable with adequate preparation and upskilling. Commence by acquainting yourself with AI fundamentals through online courses, acquire practical experience via projects, and network with industry peers. During the transition, emphasize transferable skills such as problem-solving, critical thinking, and analytical prowess.
Artificial intelligence harbors the potential for peril if not meticulously regulated and ethically developed. Concerns encompass job displacement due to automation, biases in algorithms engendering discriminatory outcomes, privacy encroachments, and the potential weaponization of AI systems. Nonetheless, with responsible development and oversight, AI can confer substantial benefits upon society.
The future of AI appears promising, marked by advancements across numerous sectors like healthcare, finance, and transportation. Its continued evolution is poised to revolutionize industries, enhance efficiency, and unearth novel opportunities. Nevertheless, ethical considerations, privacy concerns, and regulatory frameworks will significantly shape its trajectory.
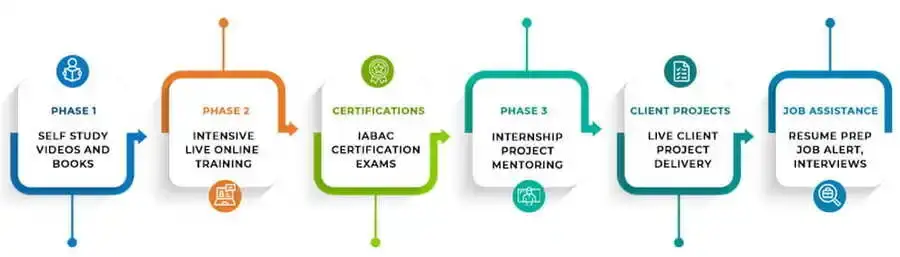
DataMites' AI Engineer Course in Poland is a 9-month program targeting intermediate and expert learners, offering career-oriented training. It aims to establish a robust foundation in machine learning and AI, covering essential topics like Python, statistics, machine learning, visual analytics, deep learning, computer vision, and natural language processing. Graduates are well-prepared to tackle real-world AI challenges effectively.
In Poland, DataMites provides AI courses with online artificial intelligence training in Poland, enabling engagement with live instructors remotely. Additionally, self-paced learning options offer flexibility, empowering learners to progress through the curriculum independently and at their own pace.
DataMites' Artificial Intelligence for Managers Course in Poland equips executives and managers with essential AI insights crucial for organizational leadership. By comprehending AI's employability and potential impact, leaders can strategically integrate AI into business operations, fostering innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage in today's dynamic business landscape.
At DataMites in Poland, career mentoring sessions for AI training are conducted in both individual and group settings. Participants receive personalized guidance on career paths, employment opportunities, skill enhancement, and industry trends, enhancing their professional development and advancement effectively.
DataMites' Artificial Intelligence Expert Training in Poland is ideal for intermediate to advanced learners, featuring a specialized 3-month program. With comprehensive modules covering core AI concepts, computer vision, and natural language processing, participants develop expert-level proficiency. Additionally, the program imparts foundational knowledge in general AI principles, ensuring graduates are well-equipped for AI career opportunities.
The fee for Artificial Intelligence Training at DataMites in Poland ranges from PLN 2,887 to PLN 7,492, depending on factors such as the chosen course, duration of training, and any additional services provided within the training package.
Individuals aspiring to enhance their AI skills in Poland can turn to DataMites, a prestigious global training institute renowned for its exceptional courses in data science and artificial intelligence.
In Poland, DataMites provides a comprehensive array of AI certifications, including roles such as Artificial Intelligence Engineer, Artificial Intelligence Expert, and Certified NLP Expert. Additionally, they offer tailored courses for managerial positions such as AI for Managers. For beginners, their Foundation program enables acquisition of fundamental knowledge and skills, paving the way for a successful AI career.
The AI Foundation Course in Poland serves as an entry point to AI education, catering to individuals from diverse backgrounds. It offers a comprehensive overview of AI applications, explaining fundamental concepts such as machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks, laying a solid groundwork for further learning and specialization in the field.
At DataMites, artificial intelligence training courses in Poland emphasize a case study-driven approach. The curriculum, intricately designed by skilled content teams, aligns with industry standards, delivering a practical learning experience geared towards job readiness and effective preparation for real-world complexities.
At DataMites Poland, AI training sessions in Poland are conducted by Ashok Veda and Lead Mentors, esteemed for their expertise in Data Science and AI. They offer exceptional mentorship, supplemented by elite mentors and faculty members from esteemed institutions like IIMs, enriching the learning journey.
In Poland, the Flexi-Pass for AI training ensures convenience, allowing learners to customize their study routine. With access to live sessions and recorded resources, participants can learn at their own pace, accommodating personal commitments and optimizing their learning experience effectively.
Yes, upon successful completion of Artificial Intelligence Training in Poland at DataMites, participants will receive IABAC Certification. This esteemed credential, adhering to the EU framework and industry guidelines, validates their skills and enhances their professional credibility internationally.
Yes, DataMites includes live projects in the Artificial Intelligence Course in Poland, comprising 10 Capstone projects and 1 Client Project. These projects offer practical application of AI concepts, equipping participants with valuable hands-on experience to excel in the field.
Yes, DataMites offers Artificial Intelligence Courses with Internship in Poland. Participants gain real-time experience in Analytics, Data Science, and AI roles within selected industries, providing valuable hands-on experience crucial for their career advancement and skill development.
Eligibility for DataMites' AI training in Poland extends to individuals with backgrounds in computer science, engineering, mathematics, or related disciplines. The program is also open to candidates from non-technical backgrounds, ensuring inclusivity and accessibility for aspiring AI professionals with diverse educational backgrounds.
Certainly, prospective participants have the option to attend a demo class for artificial intelligence training in Poland before committing to payment. This allows them to evaluate teaching approaches, course material, and instructor competence firsthand, ensuring alignment with their learning needs.
DataMites offers a range of payment methods for artificial intelligence course training in Poland, including cash, debit card, check, credit card, EMI, PayPal, Visa, Mastercard, American Express, or net banking, ensuring convenience in transactions.
Yes, participants are required to bring a valid photo identification proof, such as a national ID card or driver's license, to artificial intelligence sessions in Poland. This facilitates issuance of the participation certificate and aids in scheduling certification exams.
DataMites' artificial intelligence training courses in Poland offer flexible durations, ranging from 1 to 9 months, catering to different learning preferences and objectives. Participants can select a timeframe aligning with their schedules and desired depth of learning. Moreover, training sessions are available on weekdays and weekends, accommodating diverse schedules effectively.
The DataMites Placement Assistance Team(PAT) facilitates the aspirants in taking all the necessary steps in starting their career in Data Science. Some of the services provided by PAT are: -
The DataMites Placement Assistance Team(PAT) conducts sessions on career mentoring for the aspirants with a view of helping them realize the purpose they have to serve when they step into the corporate world. The students are guided by industry experts about the various possibilities in the Data Science career, this will help the aspirants to draw a clear picture of the career options available. Also, they will be made knowledgeable about the various obstacles they are likely to face as a fresher in the field, and how they can tackle.
No, PAT does not promise a job, but it helps the aspirants to build the required potential needed in landing a career. The aspirants can capitalize on the acquired skills, in the long run, to a successful career in Data Science.