Instructor Led Live Online
Self Learning + Live Mentoring
Customize Your Training

MODULE 1: DATA ANALYSIS FOUNDATION
• Data Analysis Introduction
• Data Preparation for Analysis
• Common Data Problems
• Various Tools for Data Analysis
• Evolution of Analytics domain
MODULE 2: CLASSIFICATION OF ANALYTICS
• Four types of the Analytics
• Descriptive Analytics
• Diagnostics Analytics
• Predictive Analytics
• Prescriptive Analytics
• Human Input in Various type of Analytics
MODULE 3: CRIP-DM Model
• Introduction to CRIP-DM Model
• Business Understanding
• Data Understanding
• Data Preparation
• Modeling, Evaluation, Deploying,Monitoring
MODULE 4: UNIVARIATE DATA ANALYSIS
• Summary statistics -Determines the value’s center and spread.
• Measure of Central Tendencies: Mean, Median and Mode
• Measures of Variability: Range, Interquartile range, Variance and Standard Deviation
• Frequency table -This shows how frequently various values occur.
• Charts -A visual representation of the distribution of values.
MODULE 5: DATA ANALYSIS WITH VISUAL CHARTS
• Line Chart
• Column/Bar Chart
• Waterfall Chart
• Tree Map Chart
• Box Plot
MODULE 6: BI-VARIATE DATA ANALYSIS
• Scatter Plots
• Regression Analysis
• Correlation Coefficients
MODULE 1: PYTHON BASICS
• Introduction of python
• Installation of Python and IDE
• Python Variables
• Python basic data types
• Number & Booleans, strings
• Arithmetic Operators
• Comparison Operators
• Assignment Operators
MODULE 2: PYTHON CONTROL STATEMENTS
• IF Conditional statement
• IF-ELSE
• NESTED IF
• Python Loops basics
• WHILE Statement
• FOR statements
• BREAK and CONTINUE statements
MODULE 3: PYTHON DATA STRUCTURES
• Basic data structure in python
• Basics of List
• List: Object, methods
• Tuple: Object, methods
• Sets: Object, methods
• Dictionary: Object, methods
MODULE 4: PYTHON FUNCTIONS
• Functions basics
• Function Parameter passing
• Lambda functions
• Map, reduce, filter functions
MODULE 1 : OVERVIEW OF STATISTICS
MODULE 2 : HARNESSING DATA
MODULE 3 : EXPLORATORY DATA ANALYSIS
MODULE 4 : HYPOTHESIS TESTING
MODULE 1: COMPARISION AND CORRELATION ANALYSIS
• Data comparison Introduction,
• Performing Comparison Analysis on Data
• Concept of Correlation
• Calculating Correlation with Excel
• Comparison vs Correlation
• Hands-on case study : Comparison Analysis
• Hands-on case study Correlation Analysis
MODULE 2: VARIANCE AND FREQUENCY ANALYSIS
• Variance Analysis Introduction
• Data Preparation for Variance Analysis
• Performing Variance and Frequency Analysis
• Business use cases for Variance Analysis
• Business use cases for Frequency Analysis
MODULE 3: RANKING ANALYSIS
• Introduction to Ranking Analysis
• Data Preparation for Ranking Analysis
• Performing Ranking Analysis with Excel
• Insights for Ranking Analysis
• Hands-on Case Study: Ranking Analysis
MODULE 4: BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS
• Concept of Breakeven Analysis
• Make or Buy Decision with Break Even
• Preparing Data for Breakeven Analysis
• Hands-on Case Study: Manufacturing
MODULE 5: PARETO (80/20 RULE) ANALSYSIS
• Pareto rule Introduction
• Preparation Data for Pareto Analysis,
• Performing Pareto Analysis on Data
• Insights on Optimizing Operations with Pareto Analysis
• Hands-on case study: Pareto Analysis
MODULE 6: Time Series and Trend Analysis
• Introduction to Time Series Data
• Preparing data for Time Series Analysis
• Types of Trends
• Trend Analysis of the Data with Excel
• Insights from Trend Analysis
MODULE 7: DATA ANALYSIS BUSINESS REPORTING
• Management Information System Introduction
• Various Data Reporting formats
• Creating Data Analysis reports as per the requirements
MODULE 1: DATA ANALYTICS FOUNDATION
• Business Analytics Overview
• Application of Business Analytics
• Benefits of Business Analytics
• Challenges
• Data Sources
• Data Reliability and Validity
MODULE 2: OPTIMIZATION MODELS
• Predictive Analytics with Low Uncertainty;Case Study
• Mathematical Modeling and Decision Modeling
• Product Pricing with Prescriptive Modeling
• Assignment 1 : KERC Inc, Optimum Manufacturing Quantity
MODULE 3: PREDICTIVE ANALYTICS WITH REGRESSION
• Mathematics behind Linear Regression
• Case Study : Sales Promotion Decision with Regression Analysis
• Hands on Regression Modeling in Excel
MODULE 4: DECISION MODELING
• Predictive Analytics with High Uncertainty
• Case Study-Monte Carlo Simulation
• Comparing Decisions in Uncertain Settings
• Trees for Decision Modeling
• Case Study : Supplier Decision Modeling - Kickathlon Sports Retailer
MODULE 1: MACHINE LEARNING INTRODUCTION
• What Is ML? ML Vs AI
• ML Workflow, Popular ML Algorithms
• Clustering, Classification And Regression
• Supervised Vs Unsupervised
MODULE 2: ML ALGO: LINEAR REGRESSSION
• Introduction to Linear Regression
• How it works: Regression and Best Fit Line
• Hands-on Linear Regression with ML Tool
MODULE 3: ML ALGO: LOGISTIC REGRESSION
• Introduction to Logistic Regression;
• Classification & Sigmoid Curve
• Hands-on Logistics Regression with ML Tool
MODULE 4: ML ALGO: KNN
• Introduction to KNN; Nearest Neighbor
• Regression with KNN
• Hands-on: KNN with ML Tool
MODULE 5: ML ALGO: K MEANS CLUSTERING
• Understanding Clustering (Unsupervised)
• Introduction to KMeans and How it works
• Hands-on: K Means Clustering
MODULE 6: ML ALGO: DECISION TREE
• Decision Tree and How it works
• Hands-on: Decision Tree with ML Tool
MODULE 7: ML ALGO: SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE (SVM)
• Introduction to SVM
• How It Works: SVM Concept, Kernel Trick
• Hands-on: SVM with ML Tool
MODULE 8: ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK (ANN)
• Introduction to ANN, How It Works
• Back propagation, Gradient Descent
• Hands-on: ANN with ML Tool
MODULE 1: DATABASE INTRODUCTION
• DATABASE Overview
• Key concepts of database management
• CRUD Operations
• Relational Database Management System
• RDBMS vs No-SQL (Document DB)
MODULE 2: SQL BASICS
• Introduction to Databases
• Introduction to SQL
• SQL Commands
• MY SQL workbench installation
MODULE 3: DATA TYPES AND CONSTRAINTS
• Numeric, Character, date time data type
• Primary key, Foreign key, Not null
• Unique, Check, default, Auto increment
MODULE 4: DATABASES AND TABLES (MySQL)
• Create database
• Delete database
• Show and use databases
• Create table, Rename table
• Delete table, Delete table records
• Create new table from existing data types
• Insert into, Update records
• Alter table
MODULE 5: SQL JOINS
• Inner join, Outer Join
• Left join, Right Join
• Self Join, Cross join
• Windows Functions: Over, Partition, Rank
MODULE 6: SQL COMMANDS AND CLAUSES
• Select, Select distinct
• Aliases, Where clause
• Relational operators, Logical
• Between, Order by, In
• Like, Limit, null/not null, group by
• Having, Sub queries
MODULE 7: DOCUMENT DB/NO-SQL DB
• Introduction of Document DB
• Document DB vs SQL DB
• Popular Document DBs
• MongoDB basics
• Data format and Key methods
• MongoDB data management
MODULE 1: BIG DATA INTRODUCTION
• Big Data Overview
• Five Vs of Big Data
• What is Big Data and Hadoop
• Introduction to Hadoop
• Components of Hadoop Ecosystem
• Big Data Analytics Introduction
MODULE 2: HDFS AND MAP REDUCE
• HDFS – Big Data Storage
• Distributed Processing with Map Reduce
• Mapping and reducing stages concepts
• Key Terms: Output Format, Partitioners, Combiners, Shuffle, and Sort
MODULE 3: PYSPARK FOUNDATION
• PySpark Introduction
• Spark Configuration
• Resilient distributed datasets (RDD)
• Working with RDDs in PySpark
• Aggregating Data with Pair RDDs
MODULE 4: SPARK SQL and HADOOP HIVE
• Introducing Spark SQL
• Spark SQL vs Hadoop Hive
MODULE 1: TABLEAU FUNDAMENTALS
• Introduction to Business Intelligence & Introduction to Tableau
• Interface Tour, Data visualization: Pie chart, Column chart, Bar chart.
• Bar chart, Tree Map, Line Chart
• Area chart, Combination Charts, Map
• Dashboards creation, Quick Filters
• Create Table Calculations
• Create Calculated Fields
• Create Custom Hierarchies
MODULE 2: POWER-BI BASICS
• Power BI Introduction
• Basics Visualizations
• Dashboard Creation
• Basic Data Cleaning
• Basic DAX FUNCTION
MODULE 3: DATA TRANSFORMATION TECHNIQUES
• Exploring Query Editor
• Data Cleansing and Manipulation:
• Creating Our Initial Project File
• Connecting to Our Data Source
• Editing Rows
• Changing Data Types
• Replacing Values
MODULE 4: CONNECTING TO VARIOUS DATA SOURCES
• Connecting to a CSV File
• Connecting to a Webpage
• Extracting Characters
• Splitting and Merging Columns
• Creating Conditional Columns
• Creating Columns from Examples
• Create Data Model
Data analytics is the process of examining and interpreting large and complex data sets to extract insights and valuable information that can be used to make informed decisions and improve business outcomes. It involves using statistical and computational methods to analyze and visualize data.
Data analytics primarily involves analyzing and interpreting data to extract insights and inform decision-making, while data science involves a broader range of skills and techniques, including computer programming, machine learning, and statistical modeling, to solve complex problems and develop predictive models. Data science also involves more emphasis on data preparation and cleaning, as well as experimental design and hypothesis testing.
Yes, anyone can pursue a career in data analytics with the right skills and training. A background in math, statistics, or computer science can be helpful, but there are also many online courses, boot camps, and degree programs available to help individuals develop the necessary skills and knowledge for a career in data analytics.
Important skills for data analytics include proficiency in programming languages such as Python and SQL, knowledge of statistical and data analysis techniques, the ability to manipulate and clean data, and effective communication and visualization skills to convey insights to stakeholders. Additionally, critical thinking, problem-solving, and attention to detail are important traits for success in data analytics.
Some of the most commonly used tools and techniques in data analytics include programming languages like Python and R, data visualization tools like Tableau and Power BI, databases like MySQL and MongoDB, and machine learning libraries like sci-kit-learn and TensorFlow. Techniques such as regression analysis, clustering, and decision trees are also frequently used in data analytics.
The cost of Data Analytics training can vary depending on the institute and the level of training desired. In South Africa, the fees for Data Analytics training can range from 8986.51 ZAR to 20219.65 ZAR, with different institutes offering different rates.
For those seeking a career in the analytics industry, DataMites is an excellent choice as a training provider. Their instructors are highly knowledgeable and have industry experience, and their course curriculum is well-designed. DataMites also offers practical training through projects and internships to give students real-world experience.
Data analytics has a wide range of job opportunities across various industries, including finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and marketing. Some popular job roles in data analytics include data analyst, business analyst, data scientist, data engineer, and data architect, among others.
Data analytics can be utilized in various fields, including healthcare, finance, marketing, e-commerce, sports, social media, and many others. It can be applied to optimize business operations, improve customer experience, develop targeted marketing strategies, and make data-driven decisions in a range of industries.
The average salary of a data analyst in South Africa ranges from R 296,617 per year according to a PayScale report.
DataMites offers excellent data analyst certification training in South Africa that provides tangible evidence of your expertise in data analytics. This training equips you with the skills necessary to help companies interpret data and make informed decisions, which can open up job opportunities with well-known multinational corporations. A certification from DataMites demonstrates your ability to perform specific job roles according to professional standards, making it more valuable than a simple data analytics certificate.
The Certified Data Analyst Course in South Africa by DataMites is an excellent choice for those interested in a career in data analytics or data science, as it is a no-coding course that requires no prior programming experience. The training program is well-organized and designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter, making it an ideal choice for beginners. If you are intrigued by analytics, signing up for this course is a great way to explore the field further.
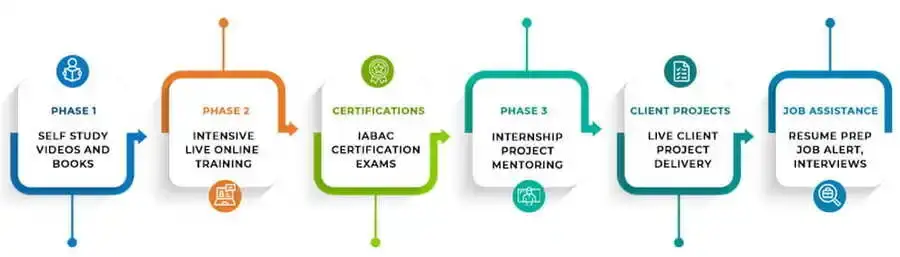
DataMites, a global institute for data science, has received approval from the International Association of Business Analytics Certifications (IABAC). They have trained over 50,000 candidates in data science and analytics, using a three-phase learning process and real-world projects and case studies to provide the best possible training. Completing the course earns an internationally recognized certification, the IABAC Data Analytics Certification and students also have the opportunity to work as an intern for Rubixe, a leading AI startup.
The cost of DataMites' certified data analytics training can vary depending on the type of training you select. Typically, in South Africa, the cost of a certified data analytics course can range from 14,205 ZAR to 26,390 ZAR depending on the mode of training.
DataMites offers six months of data analytics training, which includes 20 hours of instruction each week.
If you're considering a career as a data analyst, completing the DataMites Certified Data Analyst Training is an excellent option. Our training program is designed to provide you with a comprehensive curriculum that will equip you with the skills, certifications, and confidence to start your data analyst journey from the ground up. Rest assured that our program will give you the necessary knowledge and expertise to succeed in this field.
DataMites offers a Flexi-Pass for the Certified Data Analytics Training, allowing candidates to attend any relevant sessions within a three-month timeframe for clarification or revision purposes. This means that candidates have the flexibility to choose sessions that align with their specific needs and clear any doubts or questions they may have during the training period.
We offer multiple payment options for your convenience, including cash, debit card, check, credit card (Visa, Mastercard, American Express), PayPal, and net banking. You can choose the payment method that best suits your preference and make your payment securely and easily.
Yes, Our accreditation from IABAC® guarantees international recognition of your relevant skills and abilities. You can be confident that your training has met the required standards, and your accomplishments will be acknowledged globally.
DataMites offers a top-tier data analytics program, the Certified Data Analyst curriculum, which is accredited by the internationally recognized IABAC. Completing this course will earn you credentials from the IABAC, providing you with valuable recognition in the industry. The best way to launch a career in data analytics is by obtaining the DataMites Certified Data Analyst certification.
The DataMites Placement Assistance Team(PAT) facilitates the aspirants in taking all the necessary steps in starting their career in Data Science. Some of the services provided by PAT are: -
The DataMites Placement Assistance Team(PAT) conducts sessions on career mentoring for the aspirants with a view of helping them realize the purpose they have to serve when they step into the corporate world. The students are guided by industry experts about the various possibilities in the Data Science career, this will help the aspirants to draw a clear picture of the career options available. Also, they will be made knowledgeable about the various obstacles they are likely to face as a fresher in the field, and how they can tackle.
No, PAT does not promise a job, but it helps the aspirants to build the required potential needed in landing a career. The aspirants can capitalize on the acquired skills, in the long run, to a successful career in Data Science.