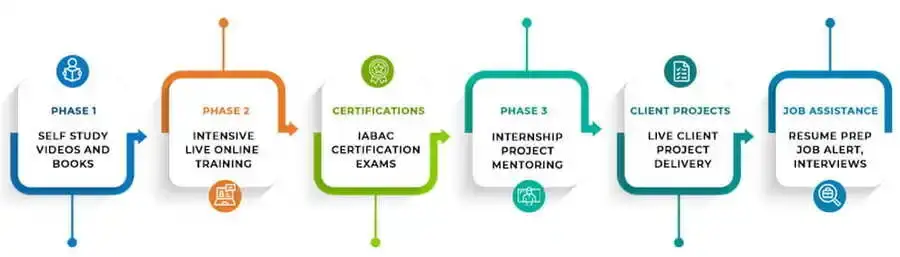
Instructor Led Live Online
Self Learning + Live Mentoring
Customize Your Training

MODULE 1: DATA SCIENCE ESSENTIALS
• Introduction to Data Science
• Evolution of Data Science
• Big Data Vs Data Science
• Data Science Terminologies
• Data Science vs AI/Machine Learning
• Data Science vs Analytics
MODULE 2: DATA SCIENCE DEMO
• Business Requirement: Use Case
• Data Preparation
• Machine learning Model building
• Prediction with ML model
• Delivering Business Value.
MODULE 3: ANALYTICS CLASSIFICATION
• Types of Analytics
• Descriptive Analytics
• Diagnostic Analytics
• Predictive Analytics
• Prescriptive Analytics
• EDA and insight gathering demo in Tableau
MODULE 4: DATA SCIENCE AND RELATED FIELDS
• Introduction to AI
• Introduction to Computer Vision
• Introduction to Natural Language Processing
• Introduction to Reinforcement Learning
• Introduction to GAN
• Introduction to Generative Passive Models
MODULE 5: DATA SCIENCE ROLES & WORKFLOW
• Data Science Project workflow
• Roles: Data Engineer, Data Scientist, ML Engineer and MLOps Engineer
• Data Science Project stages.
MODULE 6: MACHINE LEARNING INTRODUCTION
• What Is ML? ML Vs AI
• ML Workflow, Popular ML Algorithms
• Clustering, Classification And Regression
• Supervised Vs Unsupervised
MODULE 7: DATA SCIENCE INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS
• Data Science in Finance and Banking
• Data Science in Retail
• Data Science in Health Care
• Data Science in Logistics and Supply Chain
• Data Science in Technology Industry
• Data Science in Manufacturing
• Data Science in Agriculture
MODULE 1: PYTHON BASICS
• Introduction of python
• Installation of Python and IDE
• Python Variables
• Python basic data types
• Number & Booleans, strings
• Arithmetic Operators
• Comparison Operators
• Assignment Operators
MODULE 2: PYTHON CONTROL STATEMENTS
• IF Conditional statement
• IF-ELSE
• NESTED IF
• Python Loops basics
• WHILE Statement
• FOR statements
• BREAK and CONTINUE statements
MODULE 3: PYTHON DATA STRUCTURES
• Basic data structure in python
• Basics of List
• List: Object, methods
• Tuple: Object, methods
• Sets: Object, methods
• Dictionary: Object, methods
MODULE 4: PYTHON FUNCTIONS
• Functions basics
• Function Parameter passing
• Lambda functions
• Map, reduce, filter functions
MODULE 1: OVERVIEW OF STATISTICS
• Introduction to Statistics
• Descriptive And Inferential Statistics
• Basic Terms Of Statistics
• Types Of Data
MODULE 2: HARNESSING DATA
• Random Sampling
• Sampling With Replacement And Without Replacement
• Cochran's Minimum Sample Size
• Types of Sampling
• Simple Random Sampling
• Stratified Random Sampling
• Cluster Random Sampling
• Systematic Random Sampling
• Multi stage Sampling
• Sampling Error
• Methods Of Collecting Data
MODULE 3: EXPLORATORY DATA ANALYSIS
• Exploratory Data Analysis Introduction
• Measures Of Central Tendencies: Mean,Median And Mode
• Measures Of Central Tendencies: Range, Variance And Standard Deviation
• Data Distribution Plot: Histogram
• Normal Distribution & Properties
• Z Value / Standard Value
• Empirical Rule and Outliers
• Central Limit Theorem
• Normality Testing
• Skewness & Kurtosis
• Measures Of Distance: Euclidean, Manhattan And Minkowski Distance
• Covariance & Correlation
MODULE 4: HYPOTHESIS TESTING
• Hypothesis Testing Introduction
• P- Value, Critical Region
• Types of Hypothesis Testing
• Hypothesis Testing Errors : Type I And Type II
• Two Sample Independent T-test
• Two Sample Relation T-test
• One Way Anova Test
• Application of Hypothesis testing
MODULE 1: MACHINE LEARNING INTRODUCTION
• What Is ML? ML Vs AI
• Clustering, Classification And Regression
• Supervised Vs Unsupervised
MODULE 2: PYTHON NUMPY PACKAGE
• Introduction to Numpy Package
• Array as Data Structure
• Core Numpy functions
• Matrix Operations, Broadcasting in Arrays
MODULE 3: PYTHON PANDAS PACKAGE
• Introduction to Pandas package
• Series in Pandas
• Data Frame in Pandas
• File Reading in Pandas
• Data munging with Pandas
MODULE 4: VISUALIZATION WITH PYTHON - Matplotlib
• Visualization Packages (Matplotlib)
• Components Of A Plot, Sub-Plots
• Basic Plots: Line, Bar, Pie, Scatter
MODULE 5: PYTHON VISUALIZATION PACKAGE - SEABORN
• Seaborn: Basic Plot
• Advanced Python Data Visualizations
MODULE 6: ML ALGO: LINEAR REGRESSSION
• Introduction to Linear Regression
• How it works: Regression and Best Fit Line
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 7: ML ALGO: LOGISTIC REGRESSION
• Introduction to Logistic Regression
• How it works: Classification & Sigmoid Curve
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 8: ML ALGO: K MEANS CLUSTERING
• Understanding Clustering (Unsupervised)
• K Means Algorithm
• How it works : K Means theory
• Modeling in Python
MODULE 9: ML ALGO: KNN
• Introduction to KNN
• How It Works: Nearest Neighbor Concept
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 1: FEATURE ENGINEERING
• Introduction to Feature Engineering
• Feature Engineering Techniques: Encoding, Scaling, Data Transformation
• Handling Missing values, handling outliers
• Creation of Pipeline
• Use case for feature engineering
MODULE 2: ML ALGO: SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE (SVM)
• Introduction to SVM
• How It Works: SVM Concept, Kernel Trick
• Modeling and Evaluation of SVM in Python
MODULE 3: PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS (PCA)
• Building Blocks Of PCA
• How it works: Finding Principal Components
• Modeling PCA in Python
MODULE 4: ML ALGO: DECISION TREE
• Introduction to Decision Tree & Random Forest
• How it works
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 5: ENSEMBLE TECHNIQUES - BAGGING
• Introduction to Ensemble technique
• Bagging and How it works
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 6: ML ALGO: NAÏVE BAYES
• Introduction to Naive Bayes
• How it works: Bayes' Theorem
• Naive Bayes For Text Classification
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 7: GRADIENT BOOSTING, XGBOOST
• Introduction to Boosting and XGBoost
• How it works?
• Modeling and Evaluation of in Python
MODULE 1: TIME SERIES FORECASTING - ARIMA
• What is Time Series?
• Trend, Seasonality, cyclical and random
• Stationarity of Time Series
• Autoregressive Model (AR)
• Moving Average Model (MA)
• ARIMA Model
• Autocorrelation and AIC
• Time Series Analysis in Python
MODULE 2: SENTIMENT ANALYSIS
• Introduction to Sentiment Analysis
• NLTK Package
• Case study: Sentiment Analysis on Movie Reviews
MODULE 3: REGULAR EXPRESSIONS WITH PYTHON
• Regex Introduction
• Regex codes
• Text extraction with Python Regex
MODULE 4: ML MODEL DEPLOYMENT WITH FLASK
• Introduction to Flask
• URL and App routing
• Flask application – ML Model deployment
MODULE 5: ADVANCED DATA ANALYSIS WITH MS EXCEL
• MS Excel core Functions
• Advanced Functions (VLOOKUP, INDIRECT..)
• Linear Regression with EXCEL
• Data Table
• Goal Seek Analysis
• Pivot Table
• Solving Data Equation with EXCEL
MODULE 6: AWS CLOUD FOR DATA SCIENCE
• Introduction of cloud
• Difference between GCC, Azure, AWS
• AWS Service ( EC2 instance)
MODULE 7: AZURE FOR DATA SCIENCE
• Introduction to AZURE ML studio
• Data Pipeline
• ML modeling with Azure
MODULE 8: INTRODUCTION TO DEEP LEARNING
• Introduction to Artificial Neural Network, Architecture
• Artificial Neural Network in Python
• Introduction to Convolutional Neural Network, Architecture
• Convolutional Neural Network in Python
MODULE 1: DATABASE INTRODUCTION
• DATABASE Overview
• Key concepts of database management
• Relational Database Management System
• CRUD operations
MODULE 2: SQL BASICS
• Introduction to Databases
• Introduction to SQL
• SQL Commands
• MY SQL workbench installation
MODULE 3: DATA TYPES AND CONSTRAINTS
• Numeric, Character, date time data type
• Primary key, Foreign key, Not null
• Unique, Check, default, Auto increment
MODULE 4: DATABASES AND TABLES (MySQL)
• Create database
• Delete database
• Show and use databases
• Create table, Rename table
• Delete table, Delete table records
• Create new table from existing data types
• Insert into, Update records
• Alter table
MODULE 5: SQL JOINS
• Inner Join, Outer Join
• Left Join, Right Join
• Self Join, Cross join
• Windows function: Over, Partition, Rank
MODULE 6: SQL COMMANDS AND CLAUSES
• Select, Select distinct
• Aliases, Where clause
• Relational operators, Logical
• Between, Order by, In
• Like, Limit, null/not null, group by
• Having, Sub queries
MODULE 7 : DOCUMENT DB/NO-SQL DB
• Introduction of Document DB
• Document DB vs SQL DB
• Popular Document DBs
• MongoDB basics
• Data format and Key methods
MODULE 1: GIT INTRODUCTION
• Purpose of Version Control
• Popular Version control tools
• Git Distribution Version Control
• Terminologies
• Git Workflow
• Git Architecture
MODULE 2: GIT REPOSITORY and GitHub
• Git Repo Introduction
• Create New Repo with Init command
• Git Essentials: Copy & User Setup
• Mastering Git and GitHub
MODULE 3: COMMITS, PULL, FETCH AND PUSH
• Code Commits
• Pull, Fetch and Conflicts resolution
• Pushing to Remote Repo
MODULE 4: TAGGING, BRANCHING AND MERGING
• Organize code with branches
• Checkout branch
• Merge branches
• Editing Commits
• Commit command Amend flag
• Git reset and revert
MODULE 5: GIT WITH GITHUB AND BITBUCKET
• Creating GitHub Account
• Local and Remote Repo
• Collaborating with other developers
MODULE 1: BIG DATA INTRODUCTION
• Big Data Overview
• Five Vs of Big Data
• What is Big Data and Hadoop
• Introduction to Hadoop
• Components of Hadoop Ecosystem
• Big Data Analytics Introduction
MODULE 2 : HDFS AND MAP REDUCE
• HDFS – Big Data Storage
• Distributed Processing with Map Reduce
• Mapping and reducing stages concepts
• Key Terms: Output Format, Partitioners,
• Combiners, Shuffle, and Sort
MODULE 3: PYSPARK FOUNDATION
• PySpark Introduction
• Spark Configuration
• Resilient distributed datasets (RDD)
• Working with RDDs in PySpark
• Aggregating Data with Pair RDDs
MODULE 4: SPARK SQL and HADOOP HIVE
• Introducing Spark SQL
• Spark SQL vs Hadoop Hive
MODULE 1: TABLEAU FUNDAMENTALS
• Introduction to Business Intelligence & Introduction to Tableau
• Interface Tour, Data visualization: Pie chart, Column chart, Bar chart.
• Bar chart, Tree Map, Line Chart
• Area chart, Combination Charts, Map
• Dashboards creation, Quick Filters
• Create Table Calculations
• Create Calculated Fields
• Create Custom Hierarchies
MODULE 2: POWER-BI BASICS
• Power BI Introduction
• Basics Visualizations
• Dashboard Creation
• Basic Data Cleaning
• Basic DAX FUNCTION
MODULE 3 : DATA TRANSFORMATION TECHNIQUES
• Exploring Query Editor
• Data Cleansing and Manipulation:
• Creating Our Initial Project File
• Connecting to Our Data Source
• Editing Rows
• Changing Data Types
• Replacing Values
MODULE 4: CONNECTING TO VARIOUS DATA SOURCES
• Connecting to a CSV File
• Connecting to a Webpage
• Extracting Characters
• Splitting and Merging Columns
• Creating Conditional Columns
• Creating Columns from Examples
• Create Data Model
Data Science operates by gathering and examining extensive datasets to uncover patterns, trends, and insights. It utilizes statistical techniques, machine learning algorithms, and programming languages like Python or R to extract valuable information.
While a bachelor's degree in a relevant field is common, many Data Scientists hold advanced degrees such as a master's or Ph.D. Strong foundational skills in mathematics, programming, and relevant practical experience are essential.
At its core, Data Science involves extracting insights and knowledge from data through methods such as statistics, machine learning, and data analysis, encompassing the entire data lifecycle from collection to visualization.
Individuals with backgrounds in mathematics, statistics, computer science, or related disciplines are eligible for Data Science Certification Courses in New Zealand. These courses are also beneficial for professionals seeking to enhance analytical skills or transition into the field.
Statistics plays a fundamental role in data science, assisting analysts in drawing meaningful conclusions from data. It encompasses descriptive statistics for data summarization and inferential statistics for making predictions and decisions based on sampled data.
Essential skills for Data Scientists include proficiency in programming languages, data manipulation, statistical analysis, machine learning, and effective communication to convey findings.
The Certified Data Scientist Course stands out as a premier option in New Zealand, offering a comprehensive curriculum covering essential data science skills like programming, statistics, and machine learning. Participants acquire practical experience to excel in this dynamic field.
Begin by establishing a solid foundation in mathematics and programming. Gain practical experience with real-world datasets, explore data science training online in New Zealand, participate in projects, and develop a portfolio showcasing your abilities. Networking with professionals in the field can also offer valuable insights.
In finance, Data Science is crucial for tasks like risk management, fraud detection, customer segmentation, and algorithmic trading. It employs predictive modeling and analytics to optimize decision-making, enhance customer experiences, and identify irregularities in financial transactions.
Common challenges in data science projects include issues with data quality, model interpretability, and scalability. Tackling these challenges requires thorough data preprocessing, the implementation of explainable AI techniques, and optimizing algorithms for efficient processing.
Participating in Data Science Bootcamps can accelerate skill acquisition with practical experience and mentorship. Success largely depends on individual dedication and the quality of the bootcamp.
Data Science drives e-commerce success by analyzing customer behavior and transaction data, enabling personalized recommendations and enhancing user experiences. Recommendation systems, powered by machine learning, boost engagement, and sales by suggesting relevant products to shoppers.
Data Scientists collect, process, and analyze data to derive insights for strategic decision-making. They build predictive models, conduct experiments, and communicate findings to support business objectives and innovation.
Based on Glassdoor data, the average yearly salary for a Data Scientist in New Zealand stands at NZ$90,000, aligning with the national average. This reflects the market's recognition of their specialized skills in data analysis and interpretation, highlighting their pivotal role in guiding strategic decisions and fostering innovation across various industries in New Zealand.
In New Zealand, Data Scientists usually start as analysts, progressing to senior roles or specializing in areas like machine learning engineering. Career growth is fueled by continuous learning and networking.
Data Science enables retailers to analyze customer behavior and preferences, facilitating effective segmentation and personalized shopping experiences. By leveraging machine learning, businesses can optimize marketing strategies and enhance customer satisfaction.
Data Scientist Internships in New Zealand provide hands-on experience and industry insights, enhancing skill development and networking opportunities. They bolster resumes and often lead to full-time job offers.
The lifecycle of a Data Science project involves defining goals, gathering and preparing data, exploring insights, building models, validating results, deploying solutions, and ongoing monitoring. Each stage is critical for achieving business objectives and generating valuable insights.
Data Science finds extensive application across finance, healthcare, e-commerce, manufacturing, and telecommunications sectors. Its versatile methodologies and tools empower better decision-making, efficiency gains, and innovation in diverse industries.
Data Science revolutionizes manufacturing and supply chain management by predicting equipment failures, refining demand forecasts, and optimizing inventory levels. It enhances efficiency, lowers costs, and streamlines operations across the supply chain.
DataMites presents a range of data science certifications in New Zealand, including the well-known Certified Data Scientist course and specialized programs like Data Science for Managers and Data Science Associate. These cater to various skill levels and professional requirements, spanning domains such as Marketing, Operations, Finance, HR, and more.
For novices in New Zealand, DataMites delivers foundational data science training through courses like Certified Data Scientist, offering comprehensive skill sets. The Data Science in Foundation track and the Diploma in Data Science ensure a well-rounded learning experience, serving as ideal starting points for individuals venturing into the data science field.
No prerequisites are needed for enrollment in the Certified Data Scientist Training in New Zealand. Tailored for beginners and intermediate learners in data science, the course ensures accessibility for individuals aspiring to enter the field.
DataMites' data science training fee in New Zealand offers a flexible pricing model ranging from NZD 877 to NZD 2194. This ensures affordability and accommodates different budgetary preferences. The training programs cover an extensive curriculum, incorporating practical applications, making them suitable for individuals at varying proficiency levels and meeting the rising demand for skilled data scientists in New Zealand.
Enrolling in DataMites' online data science training in New Zealand provides the flexibility to learn from anywhere, overcoming geographical limitations. The interactive online platform fosters engagement through discussions, forums, and collaborative activities, enriching the overall data science training experience.
Absolutely, DataMites offers specialized data science courses in New Zealand tailored for professionals, including Statistics, Python, and Certified Data Scientist Operations. Tailored options such as Data Science with R Programming and Certified Data Scientist Courses in Marketing, HR, and Finance specifically cater to working professionals, ensuring targeted skill enhancement.
Yes, participants need to present a valid photo identification proof, such as a national ID card or driver's license, to receive their participation certificate. This documentation may also be necessary for scheduling the certification exam during the data science training sessions in New Zealand.
The DataMites Certified Data Scientist Training Course in New Zealand stands as a globally recognized program in Data Science and Machine Learning. Regularly updated to align with industry requirements, it adopts a job-oriented approach, equipping participants with vital skills and knowledge for thriving in the dynamic realm of data science.
Recognizing unforeseen circumstances, DataMites provides recorded sessions for review, allowing participants to catch up on missed content. Additionally, one-on-one sessions with trainers are available to address queries and clarify concepts covered during the missed session, ensuring a comprehensive learning experience.
Indeed, DataMites offers a trial class option in New Zealand, allowing participants to preview the training content and learning environment before making a commitment to the fee.
Trainers at DataMites are meticulously chosen based on their esteemed qualifications, with faculty members bringing real-world experience from top companies and esteemed institutes like IIMs to conduct the data science training sessions.
The duration of DataMites' data scientist courses in New Zealand ranges from 1 to 8 months, depending on the course level and specific program.
The Flexi-Pass at DataMites in New Zealand empowers participants to customize their training schedule according to their preferences, accommodating busy lifestyles and ensuring flexibility in pursuing data science training at their own pace.
For managers or leaders aiming to incorporate data science into decision-making, DataMites' "Data Science for Managers in New Zealand" course is the ideal option.
Absolutely, DataMites in New Zealand offers support sessions for participants, providing extra assistance and clarification on particular data science topics to ensure comprehensive understanding.
Upon finishing Data Science Training in New Zealand, participants receive an IABAC Certification from DataMites, recognizing their proficiency in data science.
Certainly, DataMites ensures live projects are part of their Data Scientist Course in New Zealand, including over 10 capstone projects and hands-on experience with client/live projects.
DataMites offers data science classes in New Zealand through online sessions and self-paced training methods, providing flexibility and personalized learning experiences.
Absolutely, DataMites offers Data Science Courses with internship opportunities in New Zealand, providing valuable hands-on experience with AI companies.
DataMites' career mentoring sessions in New Zealand are interactive, guiding participants on industry trends, resume building, and interview preparation to enhance their employability in the data science field.
The DataMites Placement Assistance Team(PAT) facilitates the aspirants in taking all the necessary steps in starting their career in Data Science. Some of the services provided by PAT are: -
The DataMites Placement Assistance Team(PAT) conducts sessions on career mentoring for the aspirants with a view of helping them realize the purpose they have to serve when they step into the corporate world. The students are guided by industry experts about the various possibilities in the Data Science career, this will help the aspirants to draw a clear picture of the career options available. Also, they will be made knowledgeable about the various obstacles they are likely to face as a fresher in the field, and how they can tackle.
No, PAT does not promise a job, but it helps the aspirants to build the required potential needed in landing a career. The aspirants can capitalize on the acquired skills, in the long run, to a successful career in Data Science.