Instructor Led Live Online
Self Learning + Live Mentoring
In - Person Classroom Training
The entire training includes real-world projects and highly valuable case studies.
IABAC® certification provides global recognition of the relevant skills, thereby opening opportunities across the world.
MODULE 1: DATA SCIENCE ESSENTIALS
• Introduction to Data Science
• Evolution of Data Science
• Big Data Vs Data Science
• Data Science Terminologies
• Data Science vs AI/Machine Learning
• Data Science vs Analytics
MODULE 2: DATA SCIENCE DEMO
• Business Requirement: Use Case
• Data Preparation
• Machine learning Model building
• Prediction with ML model
• Delivering Business Value.
MODULE 3: ANALYTICS CLASSIFICATION
• Types of Analytics
• Descriptive Analytics
• Diagnostic Analytics
• Predictive Analytics
• Prescriptive Analytics
• EDA and insight gathering demo in Tableau
MODULE 4: DATA SCIENCE AND RELATED FIELDS
• Introduction to AI
• Introduction to Computer Vision
• Introduction to Natural Language Processing
• Introduction to Reinforcement Learning
• Introduction to GAN
• Introduction to Generative Passive Models
MODULE 5: DATA SCIENCE ROLES & WORKFLOW
• Data Science Project workflow
• Roles: Data Engineer, Data Scientist, ML Engineer and MLOps Engineer
• Data Science Project stages.
MODULE 6: MACHINE LEARNING INTRODUCTION
• What Is ML? ML Vs AI
• ML Workflow, Popular ML Algorithms
• Clustering, Classification And Regression
• Supervised Vs Unsupervised
MODULE 7: DATA SCIENCE INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS
• Data Science in Finance and Banking
• Data Science in Retail
• Data Science in Health Care
• Data Science in Logistics and Supply Chain
• Data Science in Technology Industry
• Data Science in Manufacturing
• Data Science in Agriculture
MODULE 1: PYTHON BASICS
• Introduction of python
• Installation of Python and IDE
• Python Variables
• Python basic data types
• Number & Booleans, strings
• Arithmetic Operators
• Comparison Operators
• Assignment Operators
MODULE 2: PYTHON CONTROL STATEMENTS
• IF Conditional statement
• IF-ELSE
• NESTED IF
• Python Loops basics
• WHILE Statement
• FOR statements
• BREAK and CONTINUE statements
MODULE 3: PYTHON DATA STRUCTURES
• Basic data structure in python
• Basics of List
• List: Object, methods
• Tuple: Object, methods
• Sets: Object, methods
• Dictionary: Object, methods
MODULE 4: PYTHON FUNCTIONS
• Functions basics
• Function Parameter passing
• Lambda functions
• Map, reduce, filter functions
MODULE 1: OVERVIEW OF STATISTICS
• Introduction to Statistics
• Descriptive And Inferential Statistics
• Basic Terms Of Statistics
• Types Of Data
MODULE 2: HARNESSING DATA
• Random Sampling
• Sampling With Replacement And Without Replacement
• Cochran's Minimum Sample Size
• Types of Sampling
• Simple Random Sampling
• Stratified Random Sampling
• Cluster Random Sampling
• Systematic Random Sampling
• Multi stage Sampling
• Sampling Error
• Methods Of Collecting Data
MODULE 3: EXPLORATORY DATA ANALYSIS
• Exploratory Data Analysis Introduction
• Measures Of Central Tendencies: Mean,Median And Mode
• Measures Of Central Tendencies: Range, Variance And Standard Deviation
• Data Distribution Plot: Histogram
• Normal Distribution & Properties
• Z Value / Standard Value
• Empirical Rule and Outliers
• Central Limit Theorem
• Normality Testing
• Skewness & Kurtosis
• Measures Of Distance: Euclidean, Manhattan And Minkowski Distance
• Covariance & Correlation
MODULE 4: HYPOTHESIS TESTING
• Hypothesis Testing Introduction
• P- Value, Critical Region
• Types of Hypothesis Testing
• Hypothesis Testing Errors : Type I And Type II
• Two Sample Independent T-test
• Two Sample Relation T-test
• One Way Anova Test
• Application of Hypothesis testing
MODULE 1: MACHINE LEARNING INTRODUCTION
• What Is ML? ML Vs AI
• Clustering, Classification And Regression
• Supervised Vs Unsupervised
MODULE 2: PYTHON NUMPY PACKAGE
• Introduction to Numpy Package
• Array as Data Structure
• Core Numpy functions
• Matrix Operations, Broadcasting in Arrays
MODULE 3: PYTHON PANDAS PACKAGE
• Introduction to Pandas package
• Series in Pandas
• Data Frame in Pandas
• File Reading in Pandas
• Data munging with Pandas
MODULE 4: VISUALIZATION WITH PYTHON - Matplotlib
• Visualization Packages (Matplotlib)
• Components Of A Plot, Sub-Plots
• Basic Plots: Line, Bar, Pie, Scatter
MODULE 5: PYTHON VISUALIZATION PACKAGE - SEABORN
• Seaborn: Basic Plot
• Advanced Python Data Visualizations
MODULE 6: ML ALGO: LINEAR REGRESSSION
• Introduction to Linear Regression
• How it works: Regression and Best Fit Line
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 7: ML ALGO: LOGISTIC REGRESSION
• Introduction to Logistic Regression
• How it works: Classification & Sigmoid Curve
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 8: ML ALGO: K MEANS CLUSTERING
• Understanding Clustering (Unsupervised)
• K Means Algorithm
• How it works : K Means theory
• Modeling in Python
MODULE 9: ML ALGO: KNN
• Introduction to KNN
• How It Works: Nearest Neighbor Concept
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 1: FEATURE ENGINEERING
• Introduction to Feature Engineering
• Feature Engineering Techniques: Encoding, Scaling, Data Transformation
• Handling Missing values, handling outliers
• Creation of Pipeline
• Use case for feature engineering
MODULE 2: ML ALGO: SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE (SVM)
• Introduction to SVM
• How It Works: SVM Concept, Kernel Trick
• Modeling and Evaluation of SVM in Python
MODULE 3: PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS (PCA)
• Building Blocks Of PCA
• How it works: Finding Principal Components
• Modeling PCA in Python
MODULE 4: ML ALGO: DECISION TREE
• Introduction to Decision Tree & Random Forest
• How it works
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 5: ENSEMBLE TECHNIQUES - BAGGING
• Introduction to Ensemble technique
• Bagging and How it works
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 6: ML ALGO: NAÏVE BAYES
• Introduction to Naive Bayes
• How it works: Bayes' Theorem
• Naive Bayes For Text Classification
• Modeling and Evaluation in Python
MODULE 7: GRADIENT BOOSTING, XGBOOST
• Introduction to Boosting and XGBoost
• How it works?
• Modeling and Evaluation of in Python
MODULE 1: TIME SERIES FORECASTING - ARIMA
• What is Time Series?
• Trend, Seasonality, cyclical and random
• Stationarity of Time Series
• Autoregressive Model (AR)
• Moving Average Model (MA)
• ARIMA Model
• Autocorrelation and AIC
• Time Series Analysis in Python
MODULE 2: SENTIMENT ANALYSIS
• Introduction to Sentiment Analysis
• NLTK Package
• Case study: Sentiment Analysis on Movie Reviews
MODULE 3: REGULAR EXPRESSIONS WITH PYTHON
• Regex Introduction
• Regex codes
• Text extraction with Python Regex
MODULE 4: ML MODEL DEPLOYMENT WITH FLASK
• Introduction to Flask
• URL and App routing
• Flask application – ML Model deployment
MODULE 5: ADVANCED DATA ANALYSIS WITH MS EXCEL
• MS Excel core Functions
• Advanced Functions (VLOOKUP, INDIRECT..)
• Linear Regression with EXCEL
• Data Table
• Goal Seek Analysis
• Pivot Table
• Solving Data Equation with EXCEL
MODULE 6: AWS CLOUD FOR DATA SCIENCE
• Introduction of cloud
• Difference between GCC, Azure, AWS
• AWS Service ( EC2 instance)
MODULE 7: AZURE FOR DATA SCIENCE
• Introduction to AZURE ML studio
• Data Pipeline
• ML modeling with Azure
MODULE 8: INTRODUCTION TO DEEP LEARNING
• Introduction to Artificial Neural Network, Architecture
• Artificial Neural Network in Python
• Introduction to Convolutional Neural Network, Architecture
• Convolutional Neural Network in Python
MODULE 1: DATABASE INTRODUCTION
• DATABASE Overview
• Key concepts of database management
• Relational Database Management System
• CRUD operations
MODULE 2: SQL BASICS
• Introduction to Databases
• Introduction to SQL
• SQL Commands
• MY SQL workbench installation
MODULE 3: DATA TYPES AND CONSTRAINTS
• Numeric, Character, date time data type
• Primary key, Foreign key, Not null
• Unique, Check, default, Auto increment
MODULE 4: DATABASES AND TABLES (MySQL)
• Create database
• Delete database
• Show and use databases
• Create table, Rename table
• Delete table, Delete table records
• Create new table from existing data types
• Insert into, Update records
• Alter table
MODULE 5: SQL JOINS
• Inner Join, Outer Join
• Left Join, Right Join
• Self Join, Cross join
• Windows function: Over, Partition, Rank
MODULE 6: SQL COMMANDS AND CLAUSES
• Select, Select distinct
• Aliases, Where clause
• Relational operators, Logical
• Between, Order by, In
• Like, Limit, null/not null, group by
• Having, Sub queries
MODULE 7 : DOCUMENT DB/NO-SQL DB
• Introduction of Document DB
• Document DB vs SQL DB
• Popular Document DBs
• MongoDB basics
• Data format and Key methods
MODULE 1: GIT INTRODUCTION
• Purpose of Version Control
• Popular Version control tools
• Git Distribution Version Control
• Terminologies
• Git Workflow
• Git Architecture
MODULE 2: GIT REPOSITORY and GitHub
• Git Repo Introduction
• Create New Repo with Init command
• Git Essentials: Copy & User Setup
• Mastering Git and GitHub
MODULE 3: COMMITS, PULL, FETCH AND PUSH
• Code Commits
• Pull, Fetch and Conflicts resolution
• Pushing to Remote Repo
MODULE 4: TAGGING, BRANCHING AND MERGING
• Organize code with branches
• Checkout branch
• Merge branches
• Editing Commits
• Commit command Amend flag
• Git reset and revert
MODULE 5: GIT WITH GITHUB AND BITBUCKET
• Creating GitHub Account
• Local and Remote Repo
• Collaborating with other developers
MODULE 1: BIG DATA INTRODUCTION
• Big Data Overview
• Five Vs of Big Data
• What is Big Data and Hadoop
• Introduction to Hadoop
• Components of Hadoop Ecosystem
• Big Data Analytics Introduction
MODULE 2 : HDFS AND MAP REDUCE
• HDFS – Big Data Storage
• Distributed Processing with Map Reduce
• Mapping and reducing stages concepts
• Key Terms: Output Format, Partitioners,
• Combiners, Shuffle, and Sort
MODULE 3: PYSPARK FOUNDATION
• PySpark Introduction
• Spark Configuration
• Resilient distributed datasets (RDD)
• Working with RDDs in PySpark
• Aggregating Data with Pair RDDs
MODULE 4: SPARK SQL and HADOOP HIVE
• Introducing Spark SQL
• Spark SQL vs Hadoop Hive
MODULE 1: TABLEAU FUNDAMENTALS
• Introduction to Business Intelligence & Introduction to Tableau
• Interface Tour, Data visualization: Pie chart, Column chart, Bar chart.
• Bar chart, Tree Map, Line Chart
• Area chart, Combination Charts, Map
• Dashboards creation, Quick Filters
• Create Table Calculations
• Create Calculated Fields
• Create Custom Hierarchies
MODULE 2: POWER-BI BASICS
• Power BI Introduction
• Basics Visualizations
• Dashboard Creation
• Basic Data Cleaning
• Basic DAX FUNCTION
MODULE 3 : DATA TRANSFORMATION TECHNIQUES
• Exploring Query Editor
• Data Cleansing and Manipulation:
• Creating Our Initial Project File
• Connecting to Our Data Source
• Editing Rows
• Changing Data Types
• Replacing Values
MODULE 4: CONNECTING TO VARIOUS DATA SOURCES
• Connecting to a CSV File
• Connecting to a Webpage
• Extracting Characters
• Splitting and Merging Columns
• Creating Conditional Columns
• Creating Columns from Examples
• Create Data Model
Most data science courses are designed to be accessible to everyone, even those without prior programming experience. Although having some background in math or coding can be helpful, the most important factor is a strong willingness to learn and a genuine interest in developing data science skills. With motivation and dedication, anyone can successfully pursue a data science course.
A typical data science course in Satara usually takes 4 to 12 months to complete, depending on the course structure and the institution. Some courses offer flexible timings, allowing for part-time study. The duration may vary based on the depth and breadth of the content covered.
The entry-level salary for a data scientist in Satara is generally around INR 3 to INR 7 lakh per annum. This can vary based on the company, the candidate’s qualifications, and their experience. Salaries may increase with experience and advanced skills.
Career prospects for data science professionals in Satara are growing as businesses increasingly value data-driven decision-making. Opportunities exist in various sectors such as finance, healthcare, and technology. Skilled data scientists can expect career growth and diverse job roles.
Choosing the best data science course in Satara depends on your individual goals and needs. Seek programs that feature a robust curriculum, experienced instructors, and strong industry ties. DataMites is a leading global institute that provides internships, practical projects, strong placement support, and globally recognized certifications.
No strict coding expertise is required for a career in data science, but having programming knowledge can be beneficial. Familiarity with languages like Python or R enhances your ability to handle data manipulation, analysis, and visualization. While not mandatory, programming skills can significantly improve your effectiveness in the field.
Yes, individuals without an engineering background can become data scientists. A strong foundation in mathematics, statistics, and programming, along with relevant experience or training, can facilitate a successful transition into the field. Persistence and continuous learning are keys.
A Data Science course typically includes topics such as data analysis, machine learning, statistical methods, and data visualization. It also covers programming languages like Python or R, and tools for data manipulation. Practical projects and case studies are often part of the curriculum.
A data scientist is a professional who uses data analysis, statistical methods, and machine learning to solve complex problems and support decision-making. Their role involves collecting and interpreting large datasets, developing models, and providing insights to guide strategic actions.
To pursue a data science course in Satara, research reputable institutes that offer both online and offline options, focusing on those with internships and practical projects. DataMites offers a comprehensive data science course with practical projects, internships, and strong placement support. We also provide offline courses in cities such as Bangalore, Mumbai, Pune, Chennai, and Hyderabad.
There are no specific skills required, but having knowledge in core areas can be highly beneficial. Essential skills for a data science career include proficiency in programming languages such as Python or R. This expertise greatly enhances your ability to analyze and interpret data effectively.
Yes, data science jobs are still in demand as organizations increasingly rely on data-driven insights to make strategic decisions. The need for skilled data scientists continues to grow across various industries, including finance, healthcare, and technology.
The best methods to effectively learn data science include enrolling in structured courses, engaging in practical projects, and using online resources such as tutorials and forums. Consistent practice and staying updated with industry trends are also essential.
Yes, pursuing a career in data science is generally considered secure and stable due to the growing reliance on data for decision-making. As technology evolves, the demand for skilled data scientists is expected to continue. However, ongoing skill development is important.
The fee structure for data science courses in Satara varies depending on the institution and course duration. Fees typically range from ₹40,000 to ₹2,00,000. It’s advisable to compare courses and check for any financial assistance or payment plans.
Essential academic subjects for becoming a data scientist include mathematics, statistics, computer science, and data analysis. A strong understanding of algorithms, linear algebra, and probability is also beneficial for data science roles.
Yes, transitioning from engineering to a career in data science is feasible. Engineering backgrounds often provide strong analytical and problem-solving skills that are valuable in data science. Additional training in data science and programming can facilitate the transition.
The role of a data scientist is increasingly considered prestigious and influential in Satara due to its impact on decision-making and business strategies. Data scientists are valued for their expertise in analyzing and interpreting complex data to drive growth and innovation.
Yes, you can study data science in Satara without an extensive background in mathematics, but having a basic understanding is helpful. Many courses offer foundational training in mathematics and statistics, making the subject accessible to beginners.
Sectors increasingly adopting data science applications include finance, healthcare, retail, and technology. These industries use data science for predictive analytics, customer insights, and operational efficiency. Data science is becoming integral to various business functions.
You can enroll in the DataMites Data Science course by visiting our official website and filling out the registration form. Alternatively, you can contact our support team directly for assistance with the enrollment process.
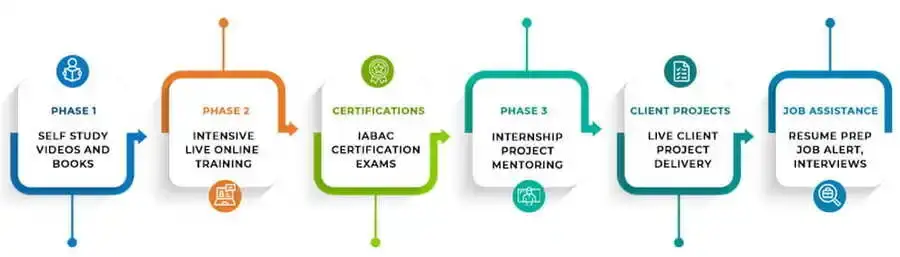
Yes, DataMites provides a Data Science course in Satara that includes 25 capstone projects and 1 client project. These projects allow students to apply their learning in real-world scenarios and gain practical experience.
Upon enrolling, you will receive course materials such as textbooks, online resources, and access to learning platforms. Additional materials like project files and software tools may also be included.
After completing the course, you will receive IABAC® & NASSCOM® FutureSkills certifications. These certifications validate your skills and knowledge in the field of data science.
Yes, DataMites offers placement assistance as part of our Data Science course in Satara. We provide support such as resume building, interview preparation, and job placement services.
DataMites includes internship opportunities as part of our Data Science course. This allows students to gain hands-on experience and apply their skills in a professional setting.
The fee for the DataMites Data Science training in Satara varies from INR 40,000 to INR80,000, based on the chosen learning mode and specific course selections. For the most accurate information, please visit the DataMites website or reach out to our support team.
Ashok Veda is the CEO of Rubixe and leads the Data Science course at DataMites. The instructors are seasoned experts with backgrounds in analytics and data science who provide to the program both real-world experience and industry understanding.
Yes, DataMites offers demo classes for prospective students. You can attend a demo session to get a preview of the course content and teaching style before making a decision.
Yes, DataMites allows students to make up missed sessions. You can access recorded classes or attend alternate sessions to ensure you cover the material.
DataMites has a refund policy for course cancellations. Eligibility for a refund depends on the terms and conditions specified at the time of enrollment.
The Flexi-Pass provides three months of flexible access to DataMites courses, allowing learners to select and switch between multiple courses during this time. This feature enables a personalized learning experience, catering to various schedules and needs. It's designed to enhance adaptability and support diverse learning preferences.
Yes, DataMites provides EMI options for our Data Science course, allowing students to pay the fee in installments. Additionally, we offer flexible payment methods including credit card, debit card, and online payment options to suit different preferences.
The Data Science syllabus at DataMites includes topics such as data analysis, machine learning, statistical methods, and data visualization. It covers both theoretical concepts and practical applications.
To enroll in the Certified Data Scientist Course, visit the DataMites website and complete the registration process. You can also contact our team for detailed enrollment assistance.
The DataMites Placement Assistance Team(PAT) facilitates the aspirants in taking all the necessary steps in starting their career in Data Science. Some of the services provided by PAT are: -
The DataMites Placement Assistance Team(PAT) conducts sessions on career mentoring for the aspirants with a view of helping them realize the purpose they have to serve when they step into the corporate world. The students are guided by industry experts about the various possibilities in the Data Science career, this will help the aspirants to draw a clear picture of the career options available. Also, they will be made knowledgeable about the various obstacles they are likely to face as a fresher in the field, and how they can tackle.
No, PAT does not promise a job, but it helps the aspirants to build the required potential needed in landing a career. The aspirants can capitalize on the acquired skills, in the long run, to a successful career in Data Science.